$20 Bonus + 25% OFF CLAIM OFFER
Place Your Order With Us Today And Go Stress-Free
Zoology is a branch of Biology dedicated to the study of Animals, both extinct and extant. This study includes morphology, physiology, geographical distribution, classification, behaviour, and embryology of animals.
Aristotle, hailed as the father of Zoology has begun the scientific study of animals. The Renaissance revived the interest in Biology and other allied disciplines. Then Zoology has gained much momentum and has reached the present era of Genomics.
Zoology throughout its development has taught humans the importance of nature’s equilibrium, and our duty as an individual in protecting nature and natural resources. It also helped him gain knowledge in the fields of medicine, agriculture and industry.
Zoology Assignment Help offers great help in understanding the concepts of Anatomy. Not only that we also help Australian students with the other branches of biological sciences.
Botany: “Plant science” is Botany. It is the study of all the features of plants, which include structure, physiology, and evolution. Click on Botany Assignment Help to know more.
Anatomy: Science of the structure of animals, plants, and humans. The two broad levels at which Anatomy is studied are Macro Anatomy/ Gross Anatomy and Micro Anatomy. To know more, check our Anatomy Assignment Help.
Biochemistry: An integral science of Biology and chemistry, which deals with the chemistry of living organisms (the metabolism or living reactions) that drives the living state of an organism. Explore our Biochemistry Assignment Help to know more.
Genomics: “Science of genes” is Genomics. This science deals with the structure, interactions, sequencing, evolutionary aspects, and mapping of genes. Want to explore more? Explore Genomics Assignment Help to know more.
Animal science is Zoology. It is the study of all the features of Animals, which includes Morphology and Anatomy, Physiology, and evolution. The Knowledge of these features helps in Animal classification, which is also an area of study in Zoology.
The following are the key branches of studies in Zoology:
Branches of Zoology based on Group Study:
Entomology: Study of Insects, that includes their structure, functions (habitat, habit and life cycle), anatomy and physiology.
Coleopterology: Study of beetles.
Dipterology: Study of Flies
Hemipterology: Study of true bugs
Isopterology: Study of Termites
Lepidopterology: Study of Butterflies
Melittology: Study of Bees.
Myrmecology: Study of Ants
Orthopterology: Study of Grasshoppers
Vespology: Study of wasps
Herpetology: Study of Amphibians and Reptiles.
Saurology: Study of Lizards
Cheloniology: Study of Tortoises
Batrachology: Study of amphibians
Mammalogy: Study of Mammals.
Primatology: Study of Primates
Cetology: Study of whales
Ornithology: Study of Birds
Parasitology: Study of parasites
Helminthology: Study of Helminths.
Planktology: Study of Plankton (microscopic animals).
Nematology: Study of Nematodes.
Arthropodology: Study of Arthropods.
Malacology: Study of Molluscs.
Branches of Zoology based on nature of study:
Anthrozoology:Ethology: Study of Animal behaviour in their natural environment.
Endocrinology: Study of endocrine systems.
Paleozoology: The study of animal fossils.
Zoogeography: Study of the distribution of animals geographically
Zoo morphology: Study of the morphology of animals.
Systematics: Taxonomy and Phylogenetics are systematics.
Animal Taxonomy: The process of identification, nomenclature, and classification of animals into groups.
Zoography: Study of animals and their habit.
Zoopathology: Study of science of diseases of animals.
Zoology is a two-sided coin, that can be approached as a basic science or as an applied science. As a basic science, it emanates the knowledge of animals, without consideration of the application.
As an applied science, it is the emanation of information that benefits both humans and animals. Zoology learnt man many things, that made his life move from a nomadic life to the life of a highly civilized one.
The scope of zoology spans the fields of Health and Disease, fields of agriculture, industry (animal products) etc. Zoology Assignment Help provides a foundation to help Australian students in learning zoology to its fullest core.
Also Read - Assignment Help Queensland
Our zoology assignment help cover the below-mentioned topics:
Evolutionary biology: This field of study looks at the origin of different species. It deals with their development and how they evolved. It also pays attention to different mechanisms like their adaptation and eating habits.
Comparative anatomy and morphology: it is the study of body parts and their functions.
It conducts its study over a range of several animal species. This helps to determine functional similarities and differences. It eventually assisted with the classification of kingdoms.
Animal Diversity: This topic explores the vast array of animal species. It interprets the classification and characteristics. It also establishes an understanding of how species interact with each other.
Population Biology: Population biology focuses on the dynamics of animal populations. It covers factors such as population and its distribution. It studies the many principles needed for a correct analysis.
Neurobiology: Neurobiology investigates the structure and function of the nervous system in animals. It studies all body parts like the brain, spinal cord, and more. This assists in understanding how they react to various interactions.
You can take the help of our zoology assignment experts and produce strong answers. They boost your grades and promote understanding. Go to our website and place an order now!
Zoology Assignment Help assists university students with more complex topics. We offer Australian students help with their assignments. We have experienced academic specialists who can be your great help.
Here is one of the advanced Zoology topics that our experts can guide you with:
A brief note on the Physiology of Kidney:
The magnificent organs Kidneys are the primary organs of filtration and have a major role in Excretion. They filter the blood and form Urine.
Filtering and Urine formation are superficially spoken functions of the Kidney. This view just overlooks the functions of Kidneys.
Kidneys perform the following primary functions.
Regulation of ionic composition: The ions regulated are sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chloride, bicarbonate, hydrogen, and phosphates.
Regulation of plasma volume and blood pressure: Kidneys can regulate the volume of urine formed. If there are disturbances in the urine formed, kidneys try to establish homeostasis by regulating blood pressure.
Regulation of Osmolarity: Kidneys can regulate the osmolarity (solute concentration) of the plasma.
Regulation of pH: Kidneys can regulate hydrogen and bicarbonate ion concentrations, which can have an impact on the pH of the blood.
Removal of metabolic waste products and foreign substances from the plasma: The metabolic by-products generated as a process of protein and nucleic acid catabolism include urea and uric acid. The wastes also include other foreign bodies. Kidneys eliminate them.
The secondary functions of Kidneys include,
Endocrine function: They secrete the hormone erythropoietin, which has a role in stimulating the bone marrow.
Renin production: Renin produced by them can stimulate the production of angiotensin – ii, which regulates blood pressure.
Activation of Vitamin D: Vitamin D is an important factor in regulating blood calcium and phosphate levels.
Basic Renal Exchange Processes:
The functions of a kidney can be broken down into three steps.
Filtration of the plasma with dissolved metabolic wastes
Reabsorption of most of the filtered plasma makes the urine more concentrated with metabolic wastes.
The urine is then stored in the urinary bladder and excreted later.
The above three steps happen in four renal processes, out of which, three are exchanges between the capillaries and the lumen.
Glomerular filtration: Bulk filtration of the blood from the glomerulus into the lumen of Bowman’s capsule.
Reabsorption: The plasma that has entered the renal tubules, enters into interstitial fluid. The plasma then re-enters into the peritubular capillaries by diffusion and is returned to the general circulation.
Secretion: The secretion of molecules from peritubular fluids into the lumen of renal tubules.
Excretion: Elimination of substances from the body in the form of urine.
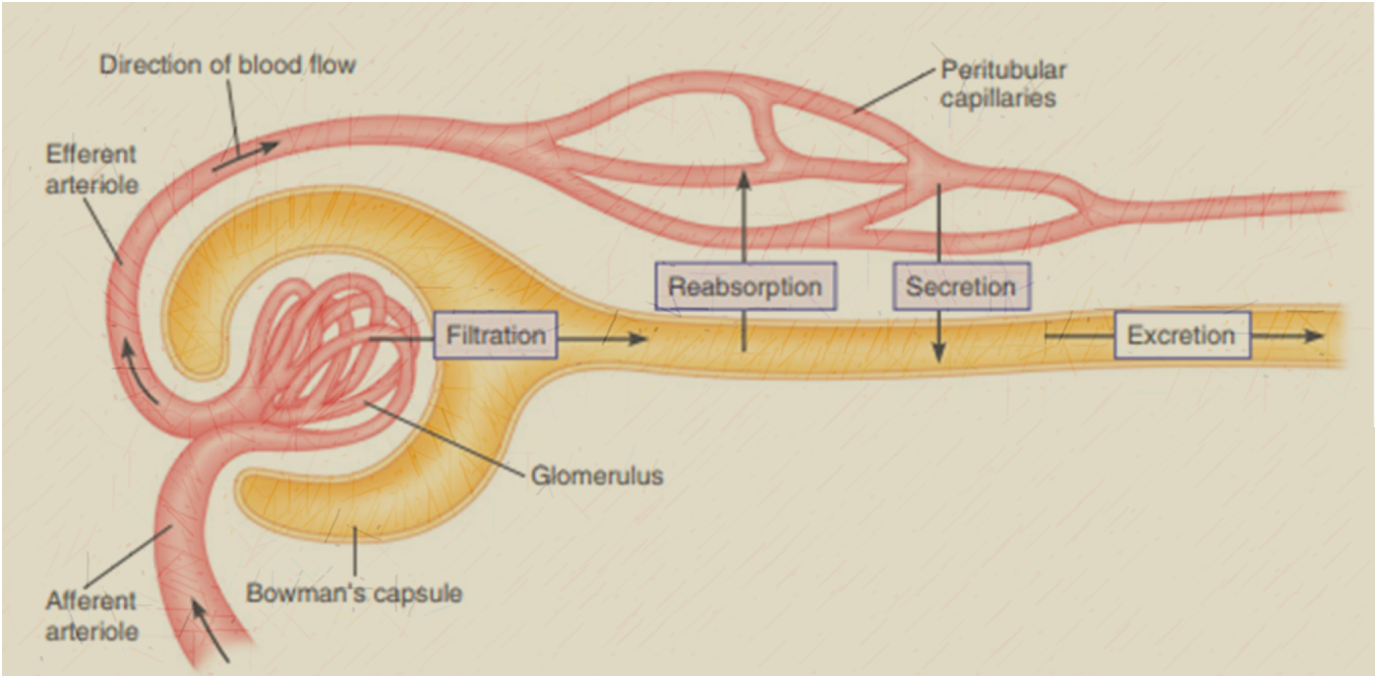
Glomerular Filtration: The blood in the glomerulus is filtered through slits formed by the interjection of three membranes into the bowman’s capsule.
The three membranes are (1) the Capillary endothelial layer, (2) the Basement membrane and (3) the podocyte layer (epithelial layer).

These three membranes make up the filtration barrier. Osmotic pressure and Hydrostatic pressure are the key forces that help in the filtration of the blood. These are four in number.
Glomerular capillary hydrostatic Pressure
Bowman’s capsule osmotic Pressure
Glomerular capillary osmotic Pressure
Bowman’s capsule hydrostatic Pressure
The forces that favour Glomerular filtration are 1. Glomerular Hydrostatic Pressure and 2. Bowman’s capsule osmotic Pressure.
The forces that oppose Glomerular filtration are 3. Glomerular osmotic Pressure and 4. Bowman’s capsule Hydrostatic Pressure.
Reabsorption: Reabsorption Is the process in which the glomerular filtrate is absorbed back into the peritubular capillaries. If there is no reabsorption, all filtered materials would be excreted, which leads to death.
The following lists the substances that are filtered and reabsorbed in a single day.
| Substances | Percentage of filtered load reabsorbed |
| Water | 99.2% |
| Glucose | 100% |
| Urea | 50% |
| Na+ | 99.4% |
| K+ | 86.1% |
| Ca2+ | 98.1% |
| Cl- | 99.2% |
| HCO3- | 99.2% |
Reabsorption mostly occurs in the proximal and distal convoluted tubules.
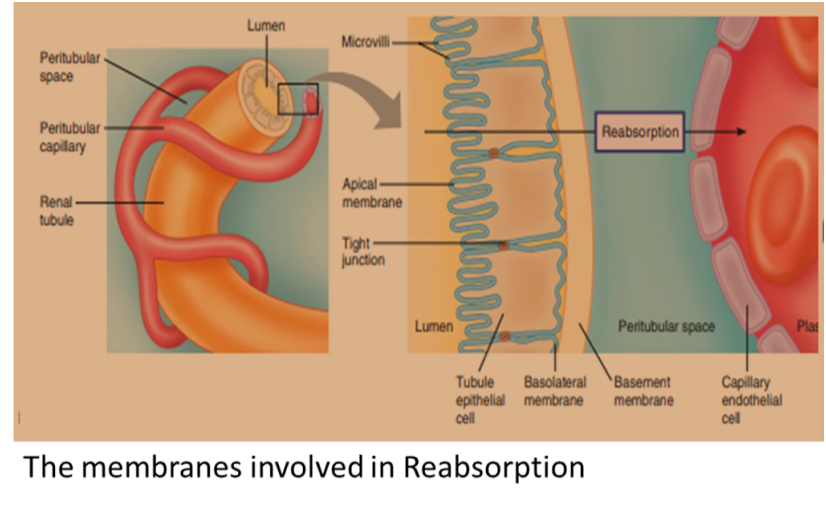
When a material is reabsorbed, it must push across two membranes, the tubule epithelium, and the capillary endothelium. Proteins cannot move through these membranes, only solutes move through these membranes. The absorption can either be active or passive.
The loop of Henle is a specialised structure evolved to conserve water. The loops of Henle are located in the renal medulla, where there is an established osmotic gradient. The osmotic gradient at the outer portion of the cortex is lower and gradually increases towards the inner portions of the medulla. This helps in the formation of concentrated Urine, with the maximum of water reabsorbed in the Loop of Henle.
Secretion:
The same basic processes follow at secretion as in reabsorption, however, this time the flow would be from peritubular capillaries into the renal tubule.
Excretion:
The waste products are eliminated in the form of solutes and a minimal amount of water.
Also Read - James Cook University Assignment Help
Classification of the Animals:
Biological classification is the scientific procedure of classifying organisms into groups and sub-groups based on similarities and dissimilarities.
Carl Linnaeus raised the animals to the level of Kingdom. But this classification was poor and included unicellular protozoans and multicellular organisms without having chlorophyll and photosynthetic ability. The better refinement to the status of the kingdom Animalia, happened in the year 1969, with the classification of Whittaker.
The Natural system of classification by R.H. Whittaker, refined the Kingdom Animalia, with its phylogeny basis. This has gained much popularity for its ease and logical approach to classifying animals.
The following are the phyla included in the Kingdom Animalia.
|
S. No. |
Phyla |
Superficial Characters of the animals |
|
1. |
Porifera |
Pore bearing, sessile, aquatic, cellular animals. |
|
2. |
Cnidaria |
First Tissue Level Organisation with stinging structures called nematocysts. |
|
3. |
Coelenterates |
No Nematocysts but have comb-like plates. |
|
4. |
Platyhelminthes |
First Organ level of organisation, Flatworms, dorsoventrally flattened |
|
5. |
Aschelminths |
The true worms with pseudocoelom. |
|
6 |
Annelida |
Vermiform and metamerically segmented body, with closed circulatory system. |
|
7 |
Arthropoda |
Animals with joined locomotory organs. |
|
8 |
Mollusca |
Body is massy, with no distinct head. No true respiratory, excretory, and nervous systems. |
|
9 |
Echinodermata |
Includes Spiny skinned animals. |
|
10 |
Hemichordata |
Worm like marine animals |
|
11 |
Chordata |
Dorsal, hollow, nerve cord, Notochord and Pharyngeal gill slits, Ventral Heart |
Before dividing them into phyla, the Kingdom Animalia is divided into the following grades, divisions and sub-divisions based on the characters listed below.
Level of Organisation (Cellular, Tissue or higher level of organisation)
Number of Germ Layers in the embryo proper.
Symmetry
An Embryological event in Blastocyst stage
Presence or Absence of coelom and the type of coelom
The prime character that divides the entire Animalia into two subkingdoms is the Level of Organisation.The Two Sub-kingdoms are:
Parazoa: Cellular level of organisation and are evolutionary blind offshoots. Example: Phylum: Porifera.
Eumetazoa: Tissue or higher level of Organisation. This is further divided into two grades, based on the symmetry/Number of Germ layers.
The two Grades are:
Grade 1: Radiata or Diploblastica: Radially Symmetrical animals, with two germ layers, Ectoderm and Endoderm filled in between with non-cellular matric Mesoglea.
Example: Phylum: Cnidaria and Ctenophora
Grade 2: Bilateria or Triploblastica: Bilaterally symmetrical animals, with three germ layers, Ectoderm, Mesoderm, and Endoderm.This grade is further divided into two divisions, based on an embryological event in the Blastocyst stage.
Division 1: Protostomia: The mouth is formed first in the embryo. The anus is formed secondarily. The presence and the type of coelom is the next character that divides this division into three sub-divisions.
Sub-division 1: Acoelomata: Coelom is the body cavity. Coelomates lack body cavities; therefore, the organs are tightly packed in them.
Example: Phylum: Platyhelminthes.
Sub-division 2: Pseudocoelomata: There is a body cavity. However, it is not true coelom. There is no lining of the mesoderm to the body cavity.
Example: Phylum: Aschelminths
Sub-division 3: Schizocoelomata: There is true coelom. The body cavity is lined by mesoderm. This coelom is a split coelom, formed by the splitting of mesoderm.
Example: Phylum: Arthropoda and Mollusca.
Division 2: Deuterostomia: The anus is formed first. Anus is formed secondarily.
Subdivision: Enterocoelomata: This is also a true coelom. The body cavity is lined by mesoderm. The coelom is formed from the embryonic mesoderm.
Example: Phylum: Hemichordata and Chordata.

Are you struggling with the concepts of Zoology? We are at your help. Our experts help you understand the concepts and drive you towards success. Expertise and In-depth Knowledge are the prime features of our experts, with which they have guided countless Australian students to ace the concepts of Zoology.
William is our faculty with M. Sc in Zoology from a reputed university and is well known for helping students teach the complex cores of a subject. He has helped many Australian students ace their assignments and got them into the tracks of the subject with ease.
Don’t miss the assistance from many learned professionals and academic experts in Zoology Assignment Help.
Also Read - Connect With Our Experts
Our website offers a wide range of free, downloadable, high-quality sample papers, designed to help you excel in your studies. Practise is what we believe in that helps in boosting the knowledge of subjects. Our Subject experts are known for their real exam-styled questions, which help you par the competitive exams with ease.
Also Read - Clinical Reasoning Cycle Assessment Help
The key points will help you write an effective Zoology assignment.
Understand the Assignment: Every Assignment revolves around some core factors. You should know your assignment’s key factors and the topics around which the assignment is centred. Make note of the instructions given, this will help you stick to the topic and leave a great impression.
Collect the Details: Utilize every available resource be it study notes, standard texts, and or websites. Get the information related to the topic in question. Collect much information on the essential factors.
Organise: Create a note of all the headers that form the body of your assignment. Introduction, sub-headings, and conclusion.
Tables and Figures: Include Tables, images and graphs wherever necessary, with appropriate descriptions.
Referencing: Referencing verifies the originality of your work and increases the reliability of the data provided.
Proofread and Edit: Revise what you have written. This will make you understand the errors in your assignment.
We offer extra help in making your Zoology assignment easier. Are you Looking for a guide or a source that could help you with your assignments? Take our help, rely on us. Look at the explanations below to understand why, to rely on us.
Expert Assistance: We offer you knowledgeable academicians who have a thorough understanding of the subject. They can address your doubts through multiple media, including messaging, phone calls, and video communication.
Approach: We don’t confuse scientific jargon but take an approach that relates topics to real-world experiences. This makes the subject understanding easier and helps retention of information.
Practice: Our adage is “Practice makes a man perfect”. We offer you a wide range of problems, tests, and mini-assignments, that can take your understanding of the subject to a new level.
Timely Delivery: Our belief is that timely delivery assistance in tests, assignments and reports ensures no future complications. We understand the importance of prompt delivery, and you can rest assured about receiving them promptly.
Confidentiality and Privacy: Your privacy is our priority; we guarantee the utmost protection of your details. Your details and identity are confidential in our system.
Originality and Authenticity: Originality is our trademark and that sets us apart from others, and the information we provide is authentic and reliable.
Affordable Pricing: We know you and your plights; we are renowned for student-friendly prices in the market.

Done Masters in Biology from the Charles Sturt University. I have worked as biology teacher for...
Masters in Biology
I have a Master's degree in Electrical and Electronics Engineering and have been working as an onl...
Masters in Electrical Engg
I have an MSc in Economics from the University of Victoria, which I completed in 2011. For the ...
MSc in Economics
Graduated from The University of Sydney with a Masters in Marketing Research. For the first fiv...
Masters in Marketing Research
My name is Sophia Sampson, and I recently earned a Ph.D. in medical science. In addition to be...
Ph.D in Medical Science
Find Best Experts in City wise
Our Best Assignment Help Expert team work.
















