$20 Bonus + 25% OFF CLAIM OFFER
Place Your Order With Us Today And Go Stress-Free
Effective risk management techniques for large scale infrastructural projects in Ireland
Large-scale infrastructure projects need effective risk management techniques.
Project performance and cost control depend on effective risk analysis.
The influence of important risk management techniques on infrastructure projects is examined in this research.
To maintain resilience and sustainability, the Ireland's infrastructure environment depends on well-informed risk management.
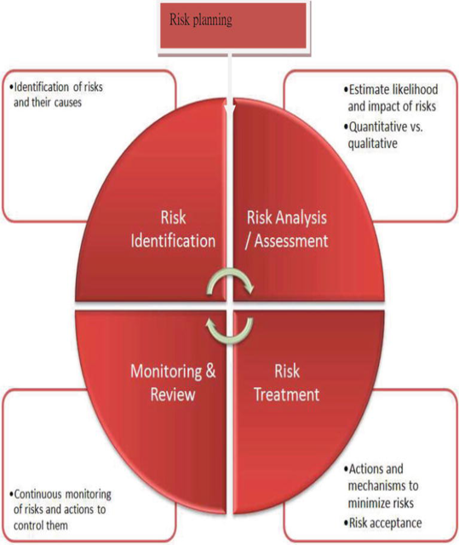
The initial aim of the research is to evaluate Effective risk management techniques for large-scale infrastructural projects in Ireland
Objective 1: To examine the areas of risk in Ireland’s large-scale projects.
Objective 2: To identify the problems faced by management teams to implement techniques of risk management.
Objective 3: To evaluate the variables impacting the risk management system externally.
Objective 4: To analyze the techniques to develop the practical implications of risk management.
RQ1: What are the potential areas of risk under large-scale projects in Ireland?
RQ2: What are the key difficulties in enhancing the effectiveness of risk management techniques?
RQ3: What are the external variables impacting Ireland’s large-scale projects?
RQ4: How can the risk management techniques be improved?
As per the academic and scientific rationale for proposing the research on discussing “effective risk management techniques for large scale infrastructural projects in Ireland” based on the advanced techniques applied by stakeholders to enhance the quality of outputs of projects. However, the research advanced technology-based techniques used to control cost and sustainability-related issues in risk management.
Risk management techniques play the most important role in project development to minimize the impact of different types of risks. Large projects in Ireland include a large number of resources which involve modelling and planning systems to provide corrective methods to reduce circumstances.
Alzoubi (2022) stated that rapid changes have included effective technology-based tools to manage project functionality. Building Information Modeling (BIM) is an important method which has been used in large construction projects to support the designing, planning and information systems.
Skilled and responsible stakeholders have been using strategic management to develop competitive advantages in resource management. Sustainability practices have included stakeholder management and cost-benefit analysis to evaluate the positive intentions of individuals connected with large projects.
Effective information technology under BIM helps project managers to identify risks related to resource management, and cost overruns to enhance sustainability. On the other hand, Simpson et al. (2021) stated the complex climate created by spatial risk patterns under projects which are solved by making effective interactions to take responsive actions to mitigate risks.
Large-scale projects involve large investments which generate adverse consequences due to neglecting effective risk management techniques. The interaction-oriented view has become an important part of risk management to adopt effective responses to improve management systems in large sectors. Therefore, developing knowledge of complex categories of risk is required to illustrate the mitigating process.
Identifying the dependent and independent variables will be the main task under the conceptual framework. Risks will be treated as the independent variables which help to analyze the effective strategies to mitigate the impacts. Strategies of risk management will be selected as dependent variables due to be dependent on the nature of risks.
However, discussing the role of stakeholders like leaders, managers and employees will be taken as mediating variables to understand the effectiveness of risk management methods (Kemshall & Maguire, 2021). Policy implementation and designing regulative bodies will play major roles in identifying the responsibility of stakeholders in Ireland’s project management.
Cost-benefit theory, stakeholder management theory and theories related to government intervention will be effective in understanding the process of preventing risks related to resource management, and financial crisis. Hu et al. (2020) stated the role of stakeholders to manage the benefits and costs of projects by taking effective calculative measures.
There are some specific roles played by stakeholders to make the risk management system manageable. Large scale constitution industry involves potential stakeholders like investors, managers and leaders to monetize the impact of risk to maintain economic benefits.
Systematic evaluations are made by stakeholders to explore cost-benefit systems. Integration of an automated system is an example of a risk management tool to develop resource management systems. Waheed & Zhang (2022) stated that ethical and cultural practices have been playing major roles in making business activities more responsible in addressing risks.
The overall study includes gaps based on risk management strategies and highlights issues with waste management, pollution management, and product quality in the existing literature.
Taking care of these gaps in huge-scope endeavours inside Ireland's framework remains an essential point. Improved sustainability methods and competitive systems, which are essential for maintaining project results and corporate implementation, will thrive if these disparities are bridged.
The primary quantitative survey method is selected for the study on potential risk management strategies for the UK’s infrastructural projects. Materials for the research will be gathered by surveying participants from the sector to collect relevant quantitative information.
The overall surveying of participants is the selected strategy to gather quantitative information related to risk management. There will be closed-end questions asked to the participants based on a primary quantitative to collect information related to management techniques applied by skilled leaders.
The primary quantitative data collection method will be used to gain numerical aspects based on 30 participants' perspectives.
There will be a specific period selected for gathering information from participants to maintain time consumption in each step of the research.
An effective automation system will be used to compile information by conducting the survey process. Information will be exported after the completion of the survey.
The nature of the survey is primary which will be designed in an effective digital format to provide user user-friendly way to collect information.
Developing a digital consent form will be the most vital part of surveying to maintain ethical consideration.
Questions will be designed by focusing on the numerical and ranking perspectives to maintain the quantitativeness of questions. There will be risk-related questions asked in the survey.
Goggle form will be the software selected for analysing the collected quantitative information. Using the tool, large databases can be evaluated including statistical forms of interpretation.
The study will be conducted by maintaining ethical guidelines which involve data security for the participants. Ethical Guidelines of organisations will be maintained by obtaining approvals from institutional authorities. In this research, the copyright law will be strictly adhered to in the complete research methodology based on the Data Protection Act, GDPR 2018.
Using statistical tools like Google Forms will help to include the aspects of the survey to identify missing values.
As per the standard scientific guidelines, the reporting system will be conducted to maintain transparency and authenticity.
Examine the methods of risk management.
Determine the difficulties and shortfalls in the current risk management techniques.
Examine how external variables affect risk management.
Provide practical ways to improve risk management (Huang, et al. 2020).

Risk assessment and mitigation techniques can be used here.
Here, risk management will be defined through cost-benefit analysis.
Interacting and corresponding with stakeholders is a crucial aspect of this study.
Government regulations and policies affect risk management in major infrastructure projects (Zhou, & Yang, 2020).

Quantitative-method research is used to blend case studies.
When evaluating the development and efficacy of risk management techniques over time, pay particular attention to longitudinal studies.
Involve stakeholders to obtain a range of viewpoints.
Identify best practices and common difficulties by doing a comparative analysis.

Examine past data on infrastructure projects
30 project leaders will be taken to ask questions (King, et al. 2021).
Ask question about risk assessment, and the mitigation process.
Analyze how government rules and stakeholder participation affect risk mitigation.

Evaluate how well risk management procedures are implemented (Afzal, et al. 2021).
Analyze how government rules and stakeholder participation affect risk mitigation.
Assess the success of risk management techniques.

Proactive risk identification and mitigation resulted in a 20% reduction in project delays.
Because of thorough financial risk assessment and backup plans, cost overruns were reduced by 15%. (Ruangpan, et al. 2020)
Involving stakeholders helped to reduce political and regulatory risks and improve project resilience.
Risk management became more successful because of risk communication.

Try to avoid conflicts of interest and guarantee impartiality in decision-making,
Upholding ethical norms requires holding accountable those who take responsibility for their choices and actions (Freddi, et al. 2021).
Large-scale infrastructure projects' possible environmental effects should be considered.

Not enough historical data to provide a thorough study (Alzoubi, 2022).
Large-scale projects with fewer participants might not be representative.
Risk management tactics may be impacted by global, political, and economic events.
Due to Ireland-specific characteristics, the findings might not be applicable worldwide.

Cooperate with professionals in the field (Rubinato, et al. 2019).
Update risk assessments on a regular basis.
Make use of sophisticated project management resources.
Place a focus on communicating with stakeholders.

Integrated risk assessment is necessary.
Constant observation is essential.
Interaction between stakeholders is essential
Resilience and backup plans are essential to the success of major infrastructure projects in the Ireland.
Alzoubi, H. M. (2022). BIM as a tool to optimize and manage project risk management. International Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 7(1). Retrieved from: https://research.skylineuniversity.ac.ae/id/eprint/192/1/63.pdf [retrieved on: 15.11.2023]
Hu, R., Iturralde, K., Linner, T., Zhao, C., Pan, W., Pracucci, A., & Bock, T. (2020). A simple framework for the cost–benefit analysis of single-task construction robots based on a case study of a cable-driven facade installation robot. Buildings, 11(1), 8. Retrieved from: https://www.mdpi.com/2075-5309/11/1/8/pdf [retrieved on: 15.11.2023]
Kemshall, H., & Maguire, M. (2021). Public protection, partnership and risk penality: The multi-agency risk management of sexual and violent offenders. In Governing Risks (pp. 319-346). Routledge. Retrieved from: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Mike-Maguire-2/publication/258181112_Public_Protection_Partnership_and_Risk_Penality_The_Multi-Agency_Risk_Management_of_Sexual_and_Violent_Offenders/links/560284ee08aeaf867fb6b6ce/Public-Protection-Partnership-and-Risk-Penality-The-Multi-Agency-Risk-Management-of-Sexual-and-Violent-Offenders.pdf?origin=journalDetail&_tp=eyJwYWdlIjoiam91cm5hbERldGFpbCJ9 [retrieved on: 15.11.2023]
Simpson, N. P., Mach, K. J., Constable, A., Hess, J., Hogarth, R., Howden, M., ... & Trisos, C. H. (2021). A framework for complex climate change risk assessment. One Earth, 4(4), 489-501. https://www.cell.com/one-earth/pdf/S2590-3322(21)00179-2.pdf [retrieved on: 15.11.2023]
Waheed, A., & Zhang, Q. (2022). Effect of CSR and ethical practices on sustainable competitive performance: A case of emerging markets from stakeholder theory perspective. Journal of Business Ethics, 175(4), 837-855. Retrieved from: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1IUpLGUAgzczQ1X4g6RVVur1tthlHgSFi/view [retrieved on: 15.11.2023]
Are you confident that you will achieve the grade? Our best Expert will help you improve your grade
Order Now










