$20 Bonus + 25% OFF CLAIM OFFER
Place Your Order With Us Today And Go Stress-Free
Education regarding sexual and relationship health is amongst the most talked about topics in the educational space currently. It is essential to have an effective system that helps students understand the matters related to relationships and sexual health so that overall public health can be maintained in the UK.
To elaborate, this research has analysed the effectiveness of school-based health education programs on sexual and relationship health among adolescents aged 13-18 in the UK.
To make it specific, the research was conducted in a systematic research format. The author has analysed 12 research articles that meet the inclusion and exclusion criteria of the research. It has been evaluated that the UK has an RSE program to deal with sexual health information for students in schools and universities.
The RSE programs have been divided into primary and secondary education as per the understanding levels of the students according to their age group.
It has been analysed that the RSE programs have been proven to have a positive impact on the students and they are able to make informed and safe decisions related to relationship and sexual health matters.
However, a gap identified in the research is that RSE programs are not equally followed in every educational space. There are differences in professor training regarding teaching the RSE program.
Moreover, there is a gap in the use of digital media for teaching RSE programs. There is a lack of initiative towards preventing the misuse of digital media for RSE programs.
The United Kingdom's public health system is increasingly focusing on the sexual and relationship health of teens as Long (2023) highlighted the rules given by the House of Commons regarding “age appropriate” Relationships and Sex Education (RSE) to be a compulsory element, making it a legal requirement in the curriculum of both primary and secondary schools. The relevance of these issues underscores the necessity for informed decision-making about sexual health and relationships, or else it can lead to poor sexual health outcomes (Wood, et al., 2022).
The new laws requiring Relationships and Sex Education (RSE) in England represent a step forward, but they also highlight the contradiction between the importance of this type of education and the way that teachers actually provide it (Cumper, et al., 2023).
It has been examined that chlamydia, gonorrhea, and HIV are increasing sexual health issues and they are increasing among people from the age of 15 up to 24 years (National Institutes of Health, 2023).
This age group clearly states that even adolescents are being exposed to sexual health issues. Figure 1 below illustrates the number of adolescents in England who are diagnosed with Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) has increased at a concerning rate in 2020, as the cases of chlamydia, gonorrhea, genital warts, and genital herpes increased by 63%, 51%, 41% and 36% respectively (Statista, 2023).
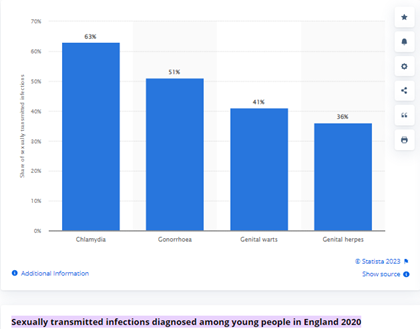
Figure 1: Sexually transmitted infections diagnosed among adolescents in England in 2020
Source: Statista, 2023
The effectiveness of Relationships and Sex Education (RSE) in England is mandated by law and relies on educators receiving adequate support and training (Cumper, et al., 2023). However, this support and training is currently insufficient. The vagueness of instructional content increases this difficulty, as emphasized by Maslowski et al. (2022).
Maslowski et al. (2023) highlighted the disjointed nature current curriculum of sex health education throughout the four constituent nations of the UK. It reported that students learn about topics such as contraception puberty and STIs within the school, however, they learn about topics such as menopause, endometriosis, and miscarriage outside the school.
This is a significant public health concern because of the growing number of STIs in young people in England, as illustrated by Figure 1. Moreover, new data given by the British Association for Sexual Health and HIV (BASHH) highlighted a 165% increase in recorded gonorrhea diagnoses over a period of 10 years (BASHH, 2023). Since the majority of the new cases involve young people, it shows that there is a lack of sexual health literacy among adolescents, making it a key public health issue.
Adolescence, the transitional phase between childhood and adulthood, is characterized by significant transformations in physical, cognitive, and social aspects. Pratt-Chapman (2020) describes this phase of adolescence as marked by a desire for autonomy, heightened influence from peers, and the exploration of sexual identity, which increases the importance of having adequate access to relationships and sex education.
Furthermore, the use of digital media is now creating certain issues for adolescents, as the study conducted by Queiroz et al. (2023) provided that digital dating sites and mobile applications allow people to have multiple partners and unprotected sex more often, which leads to increasing the number of STIs. This highlights the need for educating young people about sexual and relationship health at an early stage.
Aventin et al. (2020) highlighted the use of online and mobile technologies (OMTs) to educate parents and young people about sexual and relationship health through education programs.
However, these educational programs’ effectiveness depends on how well they can be tailored to the particular social and developmental conditions of this age group. Education can have a major impact on health outcomes and lifetime behavioral patterns in adolescents at a vital crossroads.
Therefore, school-based programs have the ability to close information gaps, debunk myths, and provide young people with the tools they need to deal with the complexities of relationships and sexual health (Meiksin et al., 2020). In light of this, it becomes necessary to evaluate how successful these educational initiatives are.
"What is the effectiveness of school-based health education programs on the sexual and relationship health of adolescents aged 13-18 in the UK?"
Bragg et al. (2022) argued that Contextually-relevant Sexuality Education creates avenues for well-informed decision-making and promotes social welfare by equipping students with knowledge, values/attitudes, and skills so that they can make informed decisions, ultimately reducing the number of STIs and influencing public health policy. The discrepancies in health outcomes are a result of the mismatch between the intended and actual implementation of RSE, which calls for a thorough assessment of these programs' efficacy (Cumper et al., 2023).
Through effective educational interventions and programs, teenagers’ behaviours, as well as health-related decision-making, are influenced, as they have the necessary knowledge to make decisions that do not adversely impact their sexual and relationship health (Van Leent et al., 2023).
However, currently, there is room for improvement in the existing sexual education programs in England, as documented by the increasing number of STIs among young people (Statista, 2023). At the same time, these educational programs have the potential to reduce these incidents, as these kinds of programs can act as a trigger to lower the incidence of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) and unintended births, improving the general health of the population (Kaltiala, et al., 2020).
However, when it comes to RSE in England, there is unequal access – particularly in low social economic classes or people living in most deprived areas where they have limited access, as a study highlighted that the UK education system “preserves inequality” rather than tackling it (Tahir, 2022).
By combining the efficacy of education with the demands of public health, this alignment has the potential to improve health equity and eventually create a society in which teenagers are capable of making informed decisions about their health (Levine, Abbruzzese, and Mason, 2022).
The research by van Leent et al. (2023) highlights the need for inclusive and comprehensive relationships and sex education, which is closely associated with better health outcomes and fewer inequities. Therefore, this research aims to evaluate the effectiveness of school-based health education programs on sexual and relationship health among Adolescents Aged 13-18 in the United Kingdom.
A systematic literature review is essential to the coordination of evidence-based practise in the field of public health. This technique is especially useful since it may condense the body of data into a coherent synthesis, clarifying trends, identifying gaps, and evaluating the overall effectiveness of current initiatives (Mohamed Shaffril, Samsuddin, and Abu Samah, 2021). Such a review is essential to guide pedagogy and policy in the field of sex education, where empirical substantiation is crucial (van Leent et al., 2023).
Policymakers and educational strategists can use the synthesis obtained from a systematic review as a compass. It makes it possible to identify evidence-based trends within the jumble of disparate programme results and instructional strategies.
Van Leent et al. (2023) have brought attention to the lack of agreement on educational techniques in sex education, which emphasises the need for a thorough review. A review like this aims to go beyond the boundaries of individual research and present a broad picture of the area (Paul and Barari, 2022).
The approach to optimising sex education programmes may be seen by doing a thorough study of aggregated data, making sure that the programmes are supported by strong pedagogical frameworks that have proven successful in a variety of settings.
A systematic review provides a thorough evaluation that can help define future educational interventions in an environment where unpredictability is the only constant (Paul and Barari, 2022).
Through a thorough analysis of the body of existing literature, this type of review serves as the foundation for evidence-based practise, which is essential for the growth of public health initiatives and the improvement of educational standards worldwide.
The primary goal of the proposed study is to assess the effectiveness of school-based health education courses on sexual and relationship health of adolescents aged 13-18 in the UK.
• To identify the key elements of RSE programs and determine who is teaching them and when by analysing various educational courses on RSE taught to adolescents.
• To assess the implication of school-based health education courses on relationship dynamics and sexual risk behaviours of adolescents.
• To analyse the actual implementation of the educational courses identified and their success rates and identifying any gaps in the provision.
The dissertation is organised to enable a logical and methodical investigation of the topic. The first chapter outlines the purpose of the research and identifies the objectives of the research. The literature review that follows summarises the body of existing research to provide insight into school-based health education initiatives, such as the RHSE committee in the United Kingdom.
It also points out areas that warrant more research. The methodology chapter follows the literature review and describes the study strategy that was used to organise the review of the literature. This section explains the search strategy, the analytical methodology used to synthesise data, and the inclusion and exclusion criteria for research.
A qualitative systematic review will be done for conducting the research and it is the most relevant approach for this research topic because it helps in identifying gaps in knowledge, highlighting research questions as well as providing evidence-based recommendations on the topic.
The results chapter summarises the findings and provides a narrative that highlights the gaps, trends, and efficacy of the existing research. A thorough discussion placing the findings in the larger context of public health and education policy is provided in the chapter. The dissertation ends with a summary of the main conclusions and contributions made during the study. It will also identify certain recommendations that can be made to solve the identified gaps.
The literature review chapter will conduct an analysis of the available literature regarding the effectiveness of school-based health education programs on sexual and relationship health in students of the UK.
Although school-based health education programs on sexual and relationship health are a mandatory part of health education in the UK, little is known about the content and effectiveness of these programs. It is also not known if the staff delivering these programs have received any specialist training to help them in this important aspect of their roles as teachers and educators.
Given this gap in the literature, it is important to undertake a literature systematic literature review to establish the evidence base in terms of sexual and relationship health education in schools in the UK. The use of available research
Also Read - Nursing Assignment Help
Over the years, there has been a change in the legal perspective towards relationship and sexual health education. As per research conducted by Cumper, et al. (2023), the legislative measures have shown the necessity of including such education in the regular curriculum of adolescent students.
RSE (Relationship and Sex Education), also referred to as RSHE (Relationship and Sexual Health Programs) is the necessary educational program to be taught by schools in their curriculum. These programs have been given mandatory status by the government since 2020 (Government UK, 2021).
This program asks the schools to share the content of such information with the parents of every student (Government UK, 2021). This step has been taken so that the parents can be aware of the ways the students are being taught and how will it impact them personally.
This program is differentiated into two perspectives. They are divided as per primary school and secondary school requirements. The primary programs are dedicated to building fundamental characteristics of positive relationships (Wilder, et al., 2020). These relationships include family, friends, or any other relation between adults and children.
Along with the basics of family relationships, these programs have certain elements for the safety of children. They include studies about personal space and boundaries, appropriate and inappropriate physical touch, and other important consent-based topics (Government UK, 2023b). Positive character traits and personal attributes are promoted in these educational programs depending on the class they are being taught in.
The progression from primary to secondary schools also includes the addition of certain necessary topics in the RSE program. The facts and laws related to sexuality, sexual health, gender identity, and other essential information are shared with adolescents in secondary schools (Government UK, 2023c). Along with this, these programs include education elements related to sexual exploitation and domestic abuse.
The behaviours, laws, protective steps, and other important safety elements are taught in these programs (Setty and Dobson, 2023). Teenage pregnancy, forced sexual relationships, sexual health issues, and other law and health topics are also covered in the secondary RSE programs in relation to public health (Government UK, 2023c).
As per research by Pratt-Chapman (2020), these programs have varied and diverse content to support the relationship and sexual health education and understanding in students. Therefore, the RSE programs have important information regarding the relationship and sexual health education for adolescent students in the UK depending on primary or secondary requirements of information.
Horan, et al. (2023) conducted research during the COVID-19 time to understand the offline and online perspectives of these educational programs. It described that RSE programs have a positive implication on young people’s sexual and relationship behaviour.
This research details that students who are educated regarding relationships and sexual health are more likely to make wise decisions about sex and relationships. They are more likely to not face health issues related to poor choices such as unintended pregnancy or sexually transmitted infections (Horan, et al., 2023).
These programs also educate students about sexual abuse and how to seek help in such cases. Therefore, it has a positive implication on the relationship and sexual health of students in the UK.
Whilst the RSE program was launched in 2020 and its official review is to be done at the end of 2023 or the start of 2024 (Government UK, 2021), some external commissions have been monitoring the programs.
A review conducted by Ofsted shows that nearly 46% of adolescent students agreed that they were not taught about the subject (Sex Education Forum, 2022). They are unaware of such a program and even for those who were aware, some of the students reported that they did not get adequate information regarding the subject.
Therefore, the implementation of these programs has to be seriously considered and necessary actions should be taken to ensure all schools are compliant with implementing these programs for their students (Horan, et al., 2023). It is also important to determine who is teaching the programs within the schools and their knowledge and experience in teaching such sensitive information.
RSE programs have given schools a right to have flexibility in their education approach towards the primary RSE programs (Government UK, 2021). It is essential to teach these programs, however, the schools have the liberty to design the curriculum in some cases as well.
However, the senior education regarding RSE programs has to be supported by the guidelines made by the RSE association. It is essential to teach the secondary programs under RSE by senior teaching management of the schools (Horan, et al., 2023).
In addition, the schools have to finalize the way in which they will draw links between the RSE subject and their regular curriculum (Government UK, 2023c). These programs have been divided into different stages to be taught by the teacher as per their qualifications.
Stages 1 and 2 are about science which includes information on external body parts, puberty, and certain changes in the human body (Government UK, 2023a). However, stages 3 and 4 are about essential information related to the relationship and sexual health. They include reproduction, menstrual cycles, gestation, HIV, AIDS, sexual health, sexual preferences, and relationship health (Government UK, 2023a).
Owing to the sensitivity of these educational programs, it is essential to deliver the information in a planned way. Students should be informed about each topic carefully so that it does not lead to any negative impact.
The PSHE Association (Personal, Social, Health and Economic) did a test on the education topic support required by the teachers to teach the RSE programs. This test was conducted on 594 teachers and the results are presented in the figure below (PSHE, 2023).
Also Read - University Of Melbourne Assignment Help

Figure 2: Educational resources required by the teachers for sexual and educational programs in schools
Source: PSHE, 2023
The above-mentioned graph illustrates the essential information sources required by the teachers of primary and secondary schools to teach the RSE programs (PSHE, 2023). This graph presents the perspectives of the teachers who are teaching RSE programs in primary and secondary program settings. This is an essential element for the research since it discusses the subjects that build up the RSE programs.
Also, the availability of study materials on these specific programs helps the teachers to assist the students regarding RSE. It is seen that well-being, mental health, sexual health, and identity are the most required readings by the teachers (PHSE, 2023). The education board in the UK has ensured that these programs are being taught by teachers specifically certified in the science and biological departments.
Along with this school nurses have been trained to help the students when in need (Government UK, 2021). RSE has been made a compulsory side subject in all schools and different external visitors have been designated for the checking process.
Along with this, the schools in the UK have been instructed by the education board to introduce lessons on pregnancy prevention and abortion in post-primary schools (Government UK, 2021). Therefore, guidelines have been made for the successful teaching implementations of the RSE programs.
A lack of such education might lead to relationship and sexual health-related issues (Purcell, et al., 2023). Having a lack of education about safety measures and healthy relationships has been a cause of many sexual issues such as teenage pregnancy, HIV, and others.
A study revealed that 8% of adolescents have faced the issues of forced sexual intercourse in a relationship (National Institutes of Health, 2023). The educational programs have strong implications on the decision-making and moral behaviours of students and therefore help them in making wise relationship and sexual health decisions.
A short survey taken by the Children’s Commission specifically in England on 3,022 children shows learnings by children related to the RHSE program. It shows the importance of having a sound education system for students that can bring positive perspectives to them (Children’s Commission, 2023).
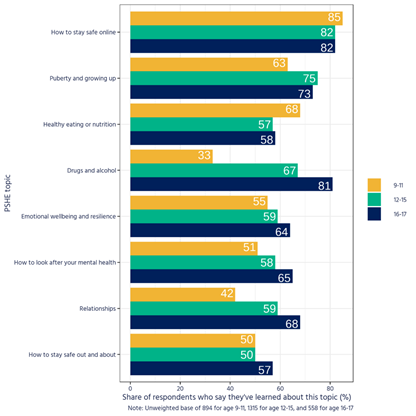
Figure 3: Examination of RSE programs in England
Source: Children's Commission, 2023
The figure above shows the implications of having a sound education system for relationship and sexual health information. Carried out on different age groups, this study shows that students are rightly influenced by the education courses when they are effectively delivered in the classrooms. The graph details the positive implications of RSE programs on preventing students from sexual risks and relationship issues and hence highlights the importance of this program.
Sexual risk behaviours in adolescent students are influenced by many factors such as family background, friend circle, religious background, country to which they belong, educational support, media, and others (Opara, et al., 2020). These risk factors are included in the educational programs and therefore, do have an impact on the decision-making of the students.
More informed and educated students might be able to take the help of other staff members or parents regarding such issues and it can save them from sexual or relationship health issues. Therefore, such information is necessary to be taught.
Effective results of these programs can be best seen when interactions in peer groups post these lessons are also considered in the curriculum. However, the literature suggests that there is no or little control over the post-peer-group discussions on the program topics (REF).
An effective regulation of knowledge-checking systems is essential (Ferfolja and Ullman, 2020). These missing elements should be addressed.
The implication of the educational courses on sexual and relationship health was analysed in research by Horan, et al. (2023). This research was conducted during the COVID-19 time to understand the offline and online perspectives of these educational programs.
It described that such educational programs have a positive implication on young people’s behaviour. Students who are educated regarding relationships and sexual health are more likely to make wise decisions about sex and relationships.
They are more likely to not face the health issues related to the same (Horan, et al., 2023). It gives students information about sexual abuse and how to seek help in such cases. Therefore, it has a positive implication on the relationship and sexual health of students in the UK.
Reviewing the implementation of these programs and their success rate is essential so that necessary further steps can be taken. The RSE program was launched in 2020 and its official review is to be done at the end of 2023 or the start of 2024 (Government UK, 2021).
However, some external commissions have been monitoring the programs. A review conducted by Ofsted on 1002 children in England shows that nearly 46% of adolescent students agreed that they were not taught about the subject (Sex Education Forum, 2022).
They are unaware of such a subject and some of the students did not get adequate information regarding the subject. Therefore, the success rate of these programs has to be seriously revised and necessary actions should be taken.
There is a need to ensure that relationship and sexual health information reaches everyone in a way that they can understand the core meanings (Bishop, et al., 2021). Along with this, section 2.3.4 shares that not every school is following these programs seriously despite them being mandatory for everyone.
Even when mandatory, as identified by Sex Education Forum (2022) 46% of the adolescent's students are not learning much about the subject. Also, similar research shows that 33% of the students did not know about the local sexual health consultation services.
There can be multiple reasons for such a case which include a lack of standardized data collection, issues with the variations of information, the quality delivered by the schools, the training of teachers, digital information, and others (McKeller and Sillence, 2020).
Therefore, there is a gap between the existence of educational programs in schools and their effective reach to students. In addition, research conducted on 16 educational professionals shows that they are in need of training for RSE (Cumper, et al., 2023).
There is a need to review the educational programs and their implementation in schools on an annual basis so that effective corrections can be made on time.
The link between mental health, sexual health, and relationship health should be explored too. Sexual and relationship health is not just about the reproductive, sexual, relationship, and sexual disease matters.
It also included many issues related to mental health and anxiety. These aspects should be linked as well as examined on the adolescent students if they are facing any of the mental challenges (Staff, et al., 2023). Creating a collaborative curriculum on sex education, relationships, and related mental health education is essential.
Also Read - Mental Health Nursing Assignment Help
The literature gap identified after conducting the literature review is that there is a knowledge gap when it comes to assessing the effectiveness of School-Based Health Education Programs on Sexual and Relationship Health among adolescent students aged 13-18 in the United Kingdom.
Some of the gaps identified in the research include the perspectives of the teachers in which they have shared that there is a need for educational material support in subjects of mental health, wellbeing, and sexual and relationship health.
As highlighted by the Sex Education Forum (2022), 46% of the children agreed that they do not know about the RSE courses; however, this calculation was done on the basis of reviews of only 1002 children from England. In addition, research conducted on 16 educational professionals shows that they are in need of training for RSE (Cumper, et al., 2023).
The perspectives of teachers as well as students from other areas were not a part of this result as well. Therefore, further research will include multiple perspectives of teachers and children across the UK.
Hence, using the qualitative systematic review system would make sure that the information regarding the effectiveness of relationship and sexual health education is to the point and has exact numbers of the possible impact. Having a study with such numerical systematic data would be helpful in creating quality research.
Along with this, it is necessary to get the information in depth regarding the causes and recommendations. The underlying causes of relationship and sexual health issues of adolescents should be examined. A current literature review does not focus on the causes of relationships and sexual desires in young adolescents.
The causes of sexual health issues in adolescents should be evaluated. Another reason that should be evaluated is regarding the issues with the RSE programs. Having knowledge of adolescent issues as well as program challenges would help in the creation of recommendations in the further chapters of the research. These elements can be covered in the systematic review.
There are two more short limitations in the literature review carried out above. It is yet to be figured out if the RSE programs are made from the perspective of adolescents with disabilities. Students with disabilities need to be educated differently. Hence it is essential to know whether these programs have a current or future scope for the training of teachers to be able to teach the disabled population of adolescents.
The research by McKeller and Sillence (2020) has certain information about the impact of digital sources, however, it does not have information regarding remedies. This aspect will be explored in further research. The review does not mention much detail about the role of digital media technologies on relationships and sexual health.
Digital media is very easily accessible and the content is open for all to watch. Therefore, it is important to know the impact of digital media and its related correction measures.
With the rise in the use of digital media and its inclusion in studies, it is also important to see if the RSE programs are being effectively delivered through online channels. The presence of the programs on digital media, their teaching techniques, and their assessment should be evaluated.
This chapter presents the research methods to be used for the collection and analysis of data for completing the research objectives. These methods will be used to find the available answers to the research question. This chapter includes various elements such as databases used for literature, keywords that have been used till now, and the keywords that will be used for analysis and collection.
The use of the SPIDER method will also be done in this chapter. The inclusion and exclusion criteria and their rationale will be explained further. A quality assessment tool (CASP) will detail the quality of the selected papers. This chapter will further include the data extraction table which will be completed in the Results section of this research.
This research will evaluate the effectiveness of relationship and sexual health education programs for adolescent children in the UK. A descriptive design has been selected to complete the research objectives (Doyle, et al., 2020). This design will evaluate the information from the available research data on authentic information databases and websites.
The data in this study is being analyzed using a single-qualitative technique. In terms of reasons this approach was chosen, it delivers more open-ended data (Bernard, 2013). This method usually prioritizes understanding complexity and breadth over mathematical representation or statistical generalizability.
It can be useful in researching several elements of student knowledge acquisition linked to relationships and sexual health. The qualitative approach is more exploratory in character, and it will provide more in-depth and insightful information gleaned from peer-reviewed research papers.
A range of journals were explored from authentic databases. These databases are Science Direct, PubMed, and Scopus. The search terms and keywords are searched by using the Boolean keyword strategy. This format uses keywords based on “and, or, not” (Ugwu and Opah, 2023).
Examples of the search keyword used for the systematic literature review here are “effective RSE”, “sexual and relationship health”, “student relationship knowledge”, “student sexual health knowledge”, “relationship and sexual health”, “student sexual knowledge”, “relationship sexual health knowledge”, “student knowledge about relationship and sexual health”, “sexual and relationship knowledge UK school”. This research section provides an outline of the research approach chosen for this study.
This is a desk-based qualitative study in which all data will be acquired from already published journal articles or peer-reviewed literature. In this study, the secondary data gathering approach will be used, which only gathers data that has previously been published. The method used to collect and assess this type of secondary material will be a systematic literature review (SLR).
Along with the databases, the information literature for the literature review was taken from some trusted websites. It includes government websites regarding the Relationship and Sexual Health education programs in the UK (Government UK, 2021). The other website sources that were used in the search are- Government UK (Relationship and Sex Education-RSE), and the Sex Education Forum UK. Using authentic sources and a limited number of databases is significant to the research since it allows for creating a niche for the data collected (Mattimoe and Hayden, 2021). It helps in keeping the research data collection to the point and helps in achieving the objectives.
| Keywords (Boolean) | Example Articles that were found |
| Relationship AND Sex Education or RSE | Horan, C., Stephenson, J. and Bailey, J.V., 2023. Relationships and Sex Education teaching in English secondary schools and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. Sex Education, pp.1-13.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/14681811.2023.2267449 |
| Mapping the reality of relationship and sex education in the UK | Holt, S.P., 2023. Mapping the reality of relationships and sex education in the UK: A phenomenographic exploration of stakeholder conceptions regarding religious and political issues affecting a school’s implementation of policy. |
| Sexual and gender minority health curricula in health care professional schools. | Pratt-Chapman, M.L., 2019. Sexual and Gender Minority Health Curricula in Health Care Professional Schools. |
The available data on relationship and sexual health education will be taken from the perspectives of adolescents in the age group of 13-18 years. Students’ education about relationships and sexual health is the main aim of the research. Only those studies that discuss the relationship and sexual health knowledge in the context of young adults or students will be selected.
The overall perspectives of the students after learning about the relationship and sexual health programs will be analysed. The impact on the decisions of the students will be analysed from the perspectives of the students, the teachers of the RSE program, and the legal authorities dealing with the RSE program.
A systematic review is being done to ensure that authentic data is included in the research. The use of available data on authentic databases would ensure that the information analysed in this research is true and to the point with the current educational environment. This systematic literature study will assess the published articles to address the research gap.
A systematic literature review will be useful in this study since it will provide the researcher with an understandable and comprehensive summary of the existing information for a given issue (Perii, 2019). This method will also indicate methodological issues in research investigations, which may be used to improve this study effort.
This systematic method helps to describe the characteristics of the group of people and its associated conditions by conducting a variety of questions. The fact that the data is analyzed using real, previously acquired data from sources with peer review strengthens the research's credibility, making the study design helpful (Mallett et al., 2012). As a result of this, the design of this study will be descriptive in nature.
The researcher analyzes the data using the thematic analysis method. Thematic analysis is the study of various patterns in data to discover meaning. It includes analyzing patterns and themes in data sets to determine underlying meaning.
This procedure is also influenced by study objectives and queries (Clarke, and Braun, 2017). As a result, instead of identifying every possible theme in data, focus on the essential research element that can link to the research objectives.
A comparison will be done between different studies on the topic of relationship and sexual health education in the UK. Through the use of a data extraction table, the author of this research will be analysing different research articles already available in the databases.
This would form a base for the analysis of the data. The information provided by different authors on the relationship and sexual health education perspectives would be compared with each other to check the similarities and differences. Later this analysis of data will be also compared to the literature review for a better systematic review outcome.
| Primary Search Terms | Synonyms | |
| S | Adolescents | Children, young age, teenagers |
| PI | Relationship and sexual health education programs | RSE, the study of sexual psychology |
| D | Qualitative systematic review | Narrative, numeric, data-based |
| E | Effectiveness of the RSE programs, strategies for implementing RSE programs | Analysis, evaluation, success-rate |
| R | Comparison analysis | Differentiating |
| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|
|
The rationale for using these criteria is that there have been many changes in the information regarding relationships and sexual health education in recent years. Digital media has turned out to be one of the major information sources in the past 10 years (Setty, 2023). Also, there has been a rise in some of the sexual health issues in adolescents.
Hence, the criteria include only recent information published from the year 2020 regarding the relationship and sexual health programs. Using the data from the year 2020 would ensure that the latest perspectives are included in the research. Since the research is focusing on the RSE programs, it is also essential to include information on the launch of the RSE programs.
The RSE programs were started in 2020 (Government UK, 2021). Hence, information before 2020 might not contribute much to the research. Also, using the latest information would ensure that the research is able to provide an up-to-date analysis of the effect of the RSE programs on the students. Due to the changing dynamics of the educational culture and background, it is better to use the latest data available.
Also, the authors who have done their research in English have been chosen to maintain language uniformity. Reflecting on the research done in English would ensure that the author is able to understand each aspect stated in available literature articles carefully. Language uniformity would also help others to read and draw out necessary data form this research when it's completed (Nyvad, Müller, and Christensen, 2022).
There will be a use of systematic research so that the information taken from already available data is fact-based and has numeric support. The use of systematic research will be helpful in conducting this new research since there is a limitation to practically collecting data from the RSE teachers. Since the RSE programs are widespread in the UK, it would be difficult for the author to practically go and collect information.
Also, having access to the information related to teachers teaching the RSE programs is not practically possible. Hence, using a systematic approach would help the author to get access to essential data without delays. This would also ensure that information from multiple authors becomes a part of the research. Therefore, through the use of a systematic approach, the current research would be able to have a detailed analysis.
Data regarding the research will be collected at the same time using the cross-sectional time horizon. Therefore, only those articles will be included in the research which fit this criteria. This means that only original articles that have been completely done and researched will be considered to be in the inclusion criteria.
To keep the data more authentic and specific, the research will only be using articles that are based on the RSE programs in the UK. Articles specific to the UK are the main boundary that has to be accepted in the inclusion criteria of the research.
Also, the research is about adolescents and hence the students in the age group of 13-18 years would be included in the research articles. Having information related to adolescent students and RSE programs would provide an in-depth understanding of the impact of the RSE programs.
To ensure the presence of authentic information, research articles that have used data specific to teachers, students, or public health authorities will only be a part of the inclusion criteria. This would also help in keeping the research close to its aims and objectives.
A section of information will also be taken from official websites along with the databases of articles. The use of official websites is being done so that factual data around matters such as sexual health, adolescents, relationship matters, sexually transmitted diseases, and other matters can be included in the research.
Factual data shared by official websites would act as a base of authentic information which will also act as a support for the findings of the research. It will be ensured that no random website or website outside the premises of the UK is used.
The papers selected in this research will be passed through the quality assessment tool of the Critical Appraisal Skills Program (Long, et al., 2020). This assessment tool first analyses the data sources through the use of ethical considerations.
The ethical considerations include the authenticity of data as well as the safe use of data by adolescents. Also, the aim of the research paper was analysed in line with the research methodology adopted. The methods for the research are selected as per the certified research tools.
Also, All relevant keywords were used across many data sources, including Taylor & Francis, Elsevier, and others. Considering the bulk of these reputable data sources are peer-reviewed, they naturally improve the standard of the selected research.
In addition, the researcher examined the uniqueness of the literature, appropriate reference use, method selection, and research gap to assess the paper's quality and reliability.
The criteria for data collection were used to finalize the data for the systematic research. The inclusion and exclusion table has further detailed the necessary elements required in the research articles for the data analysis.
The quality of these research papers will be accessed on the basis of the mentioned databases, as well as the authentic use of data by the authors. The methods chosen by the authors of the research papers in data analysis will also be screened. Also, the background information was used to understand the necessity of the current research topic on relationships and sexual education and testing its effectiveness.
| Author/ Year |
Study Design | Sample | Data Collection | Outcome |
*Complete table will be added in Chapter 4- Results
Chapter three of this research analysed the research methodologies and finalized the pathway on which the research will be done. The nature selected for the research is Descriptive. The SPIDER method, inclusion, and exclusion criteria have limited the research to systematic qualitative research that will include research taken from the time period 2020 to 2023.
The screening process is being done by adopting the PRISMA approach. PRISMA- Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (Zhang, et al., 2020).
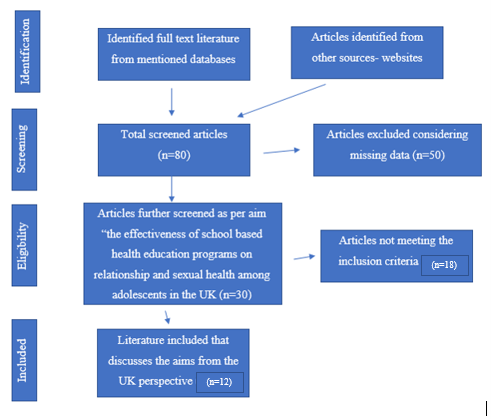
Figure 4: Prisma
Source: By author
Data analysis will be done by analysing the research articles from the data extraction tables and relating them with other key research. A comparative analysis will be done between the research done by different authors to meet the final objectives of the research.
Keywords, study sample, number of participants, limitations, and strengths of the research will be explored when calculating the results in the data extraction table. As mentioned in the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the data will be only collected through authentic sources. Research and data published from 2020 to 2023 will be a part of the data collection process only.
A systematic review will ensure that the author is able to explore different perspectives. This will help in drawing out the right information regarding the effectiveness of the RSE programs in the UK (Janssens, et al., 2020). Also, this would help in making recommendations based on the effectiveness results. Data collection would be done by using the research of authors who have information from adolescents, schools, teachers, or RSE analysts.
| Study | Author/ Year |
Study Design | Sample | Data Collection | Outcome |
| Teachers' perspectives on relationship and sex education lessons in England | Cumper, P., Adams, S., Onyejekwe, K. and O’Reilly, M. (2023) | Qualitative | 16 educational professionals | Focus Groups | There is a need for more training and support for the teachers. |
| Implementation of Sexual and gender minority health curricula in health care professional schools: a qualitative study | Pratt-Chapman, M.L. (2020) | Qualitative | 16 curricular champions | Semi-structured interviews | The inclusion of LGBTQ information helps in strengthening equality, and the RSE courses help support the sexual health of adolescents. The educational course has developed updates for diversity and inclusion. |
| Co-production of two whole school sexual health interventions for English secondary schools: positive choices and project respect | Ponsford, R., Meiksin, R., Bragg, S., Crichton, J., Emmerson, L., Tancred, T., Tilouche, N., Morgan, G., Gee, P., Young, H. and Hadley, A., (2021) | Qualitative | 75 students and 23 school staff | Formative qualitative interview | Programs address teenage pregnancy, sexual health, and other aspects. However, there is a need to allow for flexibility in timetabling of lessons. Also, parent communication is necessary. Interventions are yet limited. However, programs also focus on interpersonal, intrapersonal, and relationship education. |
| A qualitative exploration of children and young people’s experience of the secondary relationships and sex education curriculum | Cave, S. and Nicole. N. (2023). | Qualitative | 3 individuals from the RSE program | Focus Groups and Interviews | Relationship and sexual education should be given in a safe environment. This education can help adolescents in better decision-making regarding sexual and relationship matters, however, there is a lack of positive student-teacher relationships. Professionals are unsatisfactory. |
| School-based sexuality education experience across three generations of sexual minority people | Bishop, M.D., Mallory, A.B., Gessner, M., Frost, D.M. and Russell, S.T. (2021) | Qualitative | 191 people of sexual minority | Semi-structured qualitative interviews | These interviews revealed that the RSE programs help in better understanding of health issues such as HIV/AIDS. However, minorities often face shame and fear regarding discussing the topics. |
| Engaging parents in digital sexual and reproductive health education: evidence from the JACK trial. Reproductive health | Aventin, Á., Gough, A., McShane, T., Gillespie, K., O’Hare, L., Young, H., Lewis, R., Warren, E., Buckley, K. and Lohan, M. (2020). |
Qualitative | 8000 adolescents, teachers, parents, and policy experts. | Focus Groups, interviews | Digital study material and sources are engaging parents in education regarding sexual health. However, there is a lack of conversation regarding these programs with children. |
| Digital media and relationships, sex, and health education in the classroom | Setty, E. (2023) |
Qualitative | Teachers | Formative Qualitative interview | Digital media can be used to improve access to information regarding relationships and sexual health programs. However, there is a need to deal with the misuse of digital media for the same. |
| Mapping the reality of relationship and sex education in the UK. | Holt, S.P., (2023) | Qualitative Review | Academy CEO, Headteacher, RSE Lead, PSHE teacher, Parent Governor, Parent | Qualitative interviews | This education requires proper resources and funding plans. It develops skills, behaviours, critical decision-making, and effective relationships in adolescents. However, there is a lack of departmental development too. |
| Gender and Sexuality Diversity in a Culture of Limitation: Student and Teacher Experiences in Schools | Ferfolja, T. and Ullman, J. (2020). | Qualitative review | Students and Teachers of the RSE program | Focus groups, interviews | The limitations within the schools often limit the information regarding gender and sexuality diversity. |
| Relationship and sex education teaching in English secondary schools and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic | Horan, C., Stephenson, J. and Bailey, J.V. (2023). | Qualitative primary research | 16 teachers | Online semi-structured interviews | Adaptations in the RSE program are essential as per the external situations so that they can have a positive impact on the students. |
| Power, authority, and expertise: policy-making about relationships and sex education in English primary schools | Wilder, R. (2020) |
Analyzes the effectiveness of RSE programs in primary schools | Individuals who teach RSE programs, schools, policy makers | Semi-structured interviews | There is a difference between the government policies and the authorities of schools to teach the program. |
| Exploring the way sexually explicit material informs sexual beliefs, understanding and practices of young men: A qualitative survey | Peter Charles and Jane Meyrick (2021) |
Qualitative | 40 young men | Qualitative Interview | Sexually explicit materials have a negative impact on young men and a wrong idea of healthy relationships happens which is opposite to the education materials and family support. |
The above-mentioned table presents valuable information from 12 research done by different authors. This research explores different aspects related to the relationship and sexual education and their impacts on adolescents in the UK. They have included multiple perspectives such as the views of teachers, the influence on the students, the role of parents and policymakers, and the role of digital media in RSE programs.
Analysing these research articles, it can be observed that the majority of them agree that relationship and sexual health education is effective in improving decision-making skills in students. It can help prevent risks associated with unplanned sexual activities and also save adolescents from the extra pressures of relationship health matters.
Digital media plays a critical role in improving the reach of these articles and also helps the students to get better clarity on the topics. However, the misuse of digital media is a challenge to the educational implementation of the RSE programs.
An important issue highlighted in the research done by Holt (2023) shows that there are funding issues in the RSE programs. This research highlights that there is a need to create a proper budget and effective financial plans for the development of the programs. Also, funding is required so that the educational resources regarding the RSE program can be increased, this education can be reached to many schools, as well as teachers can get financial and training support.
This is also highlighted by research of Cumper, et al. (2023) where it is stated that the tutors need to have proper guidelines and training sessions. It states that through the use of training, the teachers will be able to better communicate the matters of RSE programs to the students and also help them with their queries.
Both of these research shows that there is a requirement for proper distribution of resources so that financial steps can be taken for training the teachers and providing them with the required materials. Therefore, the data analysis table highlights multiple key aspects regarding the effectiveness of relationship and sexual health education for students.
Further analysing the results as per the research by Cumper, et al. (2023), the study has highlighted the importance of RSE. This research has included the qualitative perspectives of 16 professors who have agreed that RSE programs play a major role in shaping the mindsets of the students.
They are able to make decisions regarding healthy relationships, sexual health, support, and consent (Cumper, et al., 2023). The teachers have also shared in this research that they feel such programs give spaces for open discussions and create an environment of understanding of diverse public health matters.
As per this research, diversity creation can be seen in this program since students regardless of any educational background are taught the program together. However, this research has analysed two of the most relevant challenges from the perspectives of the teachers.
These are adequate training and parental involvement. The professors in this research have mentioned that parental involvement is crucial for the success of the RSE programs. Parental objections are an issue for the programs in some cases (Cumper, et al., 2023).
Also, it is the additional responsibility of the families to foster strong relationships and educational talks at home. The second challenge is related to the training and comfort issues of the teachers. To deliver the diverse aspects of the RSE programs, the teachers have to make themselves comfortable with teaching sensitive topics.
Effective training plays an important role in delivering the program effectively which might not be the case with every teacher (Cumper, et al., 2023).
The results of the impact of RSE programs on students are also analysed in the research by Ponsford, et al. (2021) where he had a qualitative primary study on 75 students and 23 teachers. This study analyses that these programs have the influence to address and reduce teenage pregnancy issues and make students aware of sexual health. It has been analysed that these programs often discuss interpersonal and intrapersonal information.
Under the intrapersonal aspects, the programs teach about self-awareness and communication. In the interpersonal aspects, the programs discuss conflict resolutions and empathy (Ponsford, et al., 2021). However, a gap exists between the interventions and there practical account in the schools.
This research analysed that there is a lack of evidence-based support for if the students understood the topics or whether there was any interaction session or not.
In addition, there is a need to allow for flexibility in timetabling of lessons since different schools have adopted different structures of learning RSE programs that have an impact on the effectiveness due to the lack of a uniform learning structure (Ponsford, et al., 2021). Therefore, this research has highlighted that the interventions are limited and there is not much practical evidence of these implementations (Ponsford, et al., 2021).
Considering the findings of the study published by Holt (2023), there are different stakeholder perceptions for the Relationship and sex education in schools. These stakeholdrs include public health organizations, schools, universities, parents, and teachers (Holt, 2023). Along with this, there is also progress in assessing the consistency of RSE practices.
However, there are also certain challenges identified by the study including religious sustainability. considering the other findings of the study, there are differing views on whether RSE (Relationships and Sex Education) gets enough importance. Some stakeholders realize in their internal scopes the external influences put on the educational institution by wider political and social factors. Furthermore, PSHE/RSE is not evaluated and so conflicts with the way this societal issue is treated.
Teachers with no special competence in PSHE/RSE are expected to teach the topic, thereby impeding PSHE/RSE integration and development. In conclusion, while Relationship and sex education is found essential and important, it has not attained appropriate status till now and is more likely to be ignored in order to give priority to the graded subjects for which the school feels accountable (Holt, 2023).
To reflect on the impact of RSE programs on the students, the research by Cave and Nicole, et al. (2023), evaluated young people’s experience of the secondary relationship health programs. This research has highlighted the impact of RSE programs on young people’s sexual experimentation and risks.
This research has analysed that there is a gap between the teacher and student relationship which impacts the effective learnings of the programs. There is a gap in the ways students should be taught the program. A gap is also identified in the execution of the RSE programs in the research by Charles and Meyrick (2021) where it is analysed that students are getting the majority of their information about sexual and relationship matters through porn and the internet.
This research has highlighted that education has an impact on the student’s sexual experimentation, pleasures, and risks. If the programs have been taught with depth, then there are chances that the students will be positively influenced (Cave and Nicole, 2023). Therefore, it can be analysed that the type of education received by the students and the ways they are taught the programs determines the impact of RSE programs on relationships and sexual health matters.
Pratt-Chapman (2020) analysed the views of 16 curriculum experts through the use of semi-structured interviews in relation to relationship and sexual health programs. This research has been done from the perspective of examining the use of the RSE programs for gender and sexual minorities indicating diversity and inclusion. Pratt-Chapman (2020) highlights that such education can help in reducing gender-based violence cases and improve relationships.
The development of critical decision-making regarding sexual health helps the students to prevent unsafe sexual practices. An effective element that has been added to these education programs is the presence of LGBTQ+ information (Pratt-Chapman, 2020). This helps the students in accepting diversity in sexuality and also develops a justified approach towards LGBTQ+ sexuality. It has been highlighted in this study that starting the RSE programs early in elementary schools and continuing these programs throughout adolescence would help the students make the right decisions towards the inclusion of minorities and accepting diversity.
Hence, the RSE programs can be effective in delivering effective information to the students, however, they should be delivered properly. However, the research by Bishop, et al. (2021) highlights that at times gender and sexual minorities have to face shame and discrimination in the RSE programs.
There are cases where the students from the sexual minorities have to face shaming regarding their doubts about RSE in classrooms. The shaming remarks against minorities can cause a lack of interest in RSE education (Bishop, et al., 2021).
The research by Wilder (2023) analysed the presence and effectiveness of RSE programs in primary schools. There is a gap identified in the actual implementation of the RSE programs and the presence of educational matters in the RSE curriculum (Wilder, 2023).
The government has allowed schools to make certain changes in the execution of the program as required, however, it failed to design policies that can be used by the school to maintain regular education for RSE. This leads to a gap between policies and the execution of RSE (Wilder, 2023).
Avetin, et al. (2020) have analysed the importance of parent interventions in the positive impact of the RSE programs. This research was conducted on more than 8000 parents, teachers, and subject guides regarding relationship and sexual health. It has been analysed in this research that parents have access to the content of RSE programs in digital formats.
Many schools make it essential for parents to go through the programs so that they can be sure about the learnings being delivered to their children (Avetin, et al., 2020). This research highlighted that nearly 87% of parents were satisfied with the learnings being given to their children in schools related to the RSE programs. However, digital access to every content was only agreed upon by 27% of parents in this research (Avetin, et al., 2020).
Therefore, a gap is visible in the involvement of the parents in the RSE programs and their contribution to the successful understanding of these programs at the students’s homes. This aspect is important for the research objectives since the effectiveness of the RSE programs depends on teachers as well as parents of the students. Equal contribution would lead students to a better understanding of the programs.
It is essential for parents to have a conversation with their children, especially adolescents, regarding the RSE programs and their impact (Aventin, et al., 2020). This research further highlighted the importance of the parent-school relationship to optimize the benefits of the RSE programs to the students.
Setty (2022) has analysed the use of digital media in the development of RSE programs. This research evaluated that classroom discussions about the RSE programs have to be designed in a way that they are able to support the digital learning of the students.
As also highlighted by Charles and Meyrick (2020), the majority of the students are learning about relationships and sexual information through porn or wrong internet website content. The research by Setty (2022) highlights the misuse of digital media in the effectiveness of RSE programs in schools.
However, it is mentioned that if the content of the RSE programs includes the use of digital media in relationship or sexual health information, then the students will be able to have a better understanding of the educational program.
This will help in RSE programs because the learning regarding the safe use of digital media would help the students to safeguard themselves from inaccurate sexual content available digitally.
The use of digital media in the correct way can increase the reach of the RSE content across multiple students at the same time. Also, it would be easy to access and understand through the use of visual media. The only consideration is to use digital media carefully (Setty, 2022).
To focus more on the impacts of student diversity and gender, the research by Ferfolja and Ullman (2020) analysed the process of schools regarding diversity education in relation to RSE. It has been analysed in this research that school and university cultures often do not include the importance of diversity in education. Minor diversity students might feel pressure due to this and it does have an impact on their understanding of the RSE programs.
This research has further highlighted the need for training and support for the teachers in relation to gender and sexuality diversity matters so that they can improve their reach of education. It has been analysed in this research that there is a necessity to work more on diversity and also maintain the training and development of the teachers in relation to diversity and gender matters.
Horan, C., Stephenson, J. and Bailey, J.V. (2023) analysed the importance of adaptations in the RSE programs. From the perspective of the COVID-19 lockdowns, the research has analysed that it has been important for teachers to adapt the ways they teach the RSE programs. During the COVID-19 time, the lockdowns affected the regular ways of schooling.
Through the use of digital media, the schools were able to complete their educational practices (Horan, Stephenson, and Bailey, 2023). This research evaluated that teachers of the RSE program were able to adapt there teachings in reference to the COVID-19 period and therefore a positive impact was created regarding the continuity of the subject.
RSE programs were made compulsory in 2020 and after a few months, COVID-19 created issues in the continuity of the program. The research has highlighted the importance of updating the ways of teachings in response to external conditions.
Post the COVID-19 situation, schools, and universities have been relying on the digital distribution of information regarding the RSE programs. As per this research, the over-dependence on digital mediums can limit the learning of the students regarding RSE.
However, a positive aspect is that the teachers of this program are able to change their practices in response to external situations and therefore the program is able to maintain its continuity.
Overall, the analysis of each study in the data analysis table has provided essential information regarding the effectiveness and impact of the RSE programs on adolescents in the UK. More of this information will be discussed in the discussion chapter below.
The systematic review highlights the importance of the relationship and educational programs. It shows that these programs have been designed in a way that they have a positive impact on primary as well as secondary students (Ponsford, 2021). The division of information as per the age of the adolescents and their understanding capabilities helps the RSE programs reach their goals.
However, it can be observed that there has to be improved training for the teachers regarding the RSE programs and other relationship and sexual health aspects (Cumper, et al., 2023). Other research articles have also highlighted the use of RSE programs and other education initiatives to help students make wise decisions regarding their relationships and sexual health.
The knowledge and behaviours developed through RSE programs are effective in helping students in taking the correct steps regarding their relationship health (Bishop, 2021). In addition, students agreed that there are educational programs on puberty and contraception. However, there is a gap in the teacher-student relationship which has a negative impact on the learning of the program.
Also, the study material lacks in terms of requirements (Cave and Nicole, 2023). This indicates that the relationship and sexual health programs need an update in their curriculum and education resources. There has to be a review of the matters being studied in these programs and an evaluation of their need at the current time (Cave and Nicole, 2023).
The diversity of content in the RSE programs has been explored by research done by Setty and Dobson (2023). It has been analysed in this research that the program has important information related to sexual health, relationship building, behaviours of people, safety steps in sexual activities, and other laws that protects the rights of adolescents.
The laws to help the students with sexual matters have also been briefed in the program. Along with this, important issues such as teenage pregnancy and forced sexual relationships have been discussed in the program (Seety and Dobson, 2023).
The design of the RSE program includes diverse aspects related to adolescents in terms of relationships and sexual health such as gender and sexual minorities, sexual diseases, and others (Pratt-Chapman, 2020). This information is further divided into primary and secondary to make the students understand the matter as per their age understanding (Ponsford, 2021).
Despite making the program necessary, Sex Education Forum (2022) has analysed that 46% of the students are not properly aware of the topics of the program. This is also highlighted by research conducted by Horan, et al. (2023) where he analysed that serious actions should be taken to bridge the gap between the programs on paper and their actual teachings in classrooms.
It has been also shared by Purcell, et al. (2023) that a lack of information regarding relationships and sexual health can increase sexual health issues and transmitted diseases. While, with educational support, a student can deal with such situations in a much better way and prevent themselves from such diseases.
The research by Opara, et al. (2020) has stated that sexual risk behaviours can be developed in adolescents if they are not educated about the topics. They can be easily influenced by their friend circle, background, country, and other beliefs. Therefore, having RSE information can shape their influence in a positive way and help them in making critical decisions (Opara, et al., 2020).
The findings of the data analysis table show certain themes. These themes are- RSE programs have a diverse approach towards relationship and sexual health education matters, there is a lack of digital support in the program, parents need to take equal initiatives to make RSE programs a success, and teachers have a lack of training and resources regarding the RSE programs.
These 5 themes will be discussed here in relation to the available literature. Despite the regulations, these programs are not being taught properly or there is a lack of proper distribution of information in every school and university (Holt, 2023). Also, there are issues regarding the inclusion of digital sources of information regarding the RSE programs.
The same has been observed in the research of Shetty (2022) in data analysis where she has highlighted that digital media has to be used in a way that increases the reach of information as well as prevents the students from the misuse of data. The misuse of digital data for relationship and sexual matters has been shown in the research by Charles and Meyrick (2020).
This research states that the students are not utilizing the information provided in the RSE program. Rather they are being aware of these sensitive matters through digital data. A high share of information is being taken from the wrong sources of porn (Charles and Meyrick, 2020). This is a risky situation for the understanding of the RSE programs. Therefore, it is essential to find some digital solutions for the RSE program makers.
The literature review has research discussing the importance of parental initiatives on the impact of the RSE programs. Also, the official websites of RSE under Government UK (2021) have shared that the curriculum of the program is shared with the parents of the students so that they can keep track of what is being taught as well as engage in the learning process.
The importance of parent initiatives has also been shared in the research by Avetin, et al. (2020) where it is said that the use of digital sources to engage parents in the RSE programs is necessary.
Having parental guidance is essential for the students to understand the matters related to RSE effectively. However, a gap exists in parental access to the RSE program content. Aventin, et al. (2020) have shared in their research that only 27% of the parents have proper access to each content being taught to their children through the RSE program.
This is an issue regarding the implementation of the RSE program in the schools. Sharing the information with parents is essential so that they can communicate with the students as well as ensure that no misuse of content is done by the students (Aventin, et al., 2020).
Setty and Dobson (2023) have shown in their research that the RSE programs focus on diverse topics related to sexual health matters. They have included information related to safe sexual behaviour, dealing with teen pregnancy issues, taking the support of laws for safety, and others.
A similar aspect shared by Bishop, et al. (2021) has supported the above statement and explored that the RSE programs have diverse educational elements to help students be aware of multiple information related to relationships and sexual health. The study by Pratt-Chapman (2020) has also supported the idea of diversity in the RSE programs.
The research has evaluated that RSE programs have improved the diversity aspects by ensuring that LGBTQ+ sexual health matters also become a part of the study curriculum (Pratt-Chapman, 2020).
Also, this research has shown the importance of the RSE programs in reducing teenage pregnancy matters and informed decisions regarding healthy relationships. However, the research by Bishop, et al. (2021) highlights that at times gender and sexual minorities have to face shame and discrimination in the RSE programs.
This research included the views of the students regarding relationship and sexual health school programs. The students have indicated that there is an effective knowledge about relationship health, mental health, biological aspects, and others.
However, information regarding sexual health and its related aspects is not as effective (Ponsford, et al, 2021). Different research articles have highlighted different aspects of the relationship and sexual health education programs.
Some have identified that these programs have been proven to be effective in showing results in the students (Cumper, et al., 2023). They can better understand the relationship and sexual health aspects and therefore, make wise decisions.
Cumper, et al. (2023) have mainly evaluated the perspectives of the teachers regarding the RSE programs. This research has discussed that teachers are having issues regarding the delivery of content in an effective manner. This is due to the lack of training and development sessions. Training is essential to make the teachers comfortable with the program topics so that they can share the information with the students in an effective manner.
The queries of the students have to be also managed in a way that does not create separate meanings and helps them understand the topic as required by the guidelines. An important aspect regarding the training and development programs for RSE teachers has been highlighted in research by Holt (2023) where it is stated that there are issues regarding the budget and financial requirements of the program. The lack of training sessions for the teachers as well as the lack of education resources are present due to budgetary issues.
However, other research articles have highlighted certain needed to be included in the new updates of the program. There has to be an addition of digital media resources and control on how this content is used. The misuse of data can be disadvantageous for the students (Shetty, 2022). Also, the need for teachers to be trained has been highlighted (Cumper, et al., 2023).
Overall, the discussion and analysis of the literature as well as the data analysis table show some of the benefits of RSE programs. They also highlight the challenges under these programs. Benefits are related to the development of critical decision-making in students. They also develop learnings about how to prevent themselves from sexually transmitted diseases. It would also improve their healthy relationships. However, some of the challenges that have been identified are related to the budget, training of the professors of RSE, changing influence of digital media, and lack of parental efforts towards the program.
Certain limitations that occurred when doing the systematic review are related to the number of studies. It can be observed that fixing the search strategies creates a limit on the number of studies that can be used for the review. This makes the research limited and might have lacked some important information that could have been gained with a wide range of search strategies (Uttley, et al., 2023).
The limitation of search strategies, and research methods can create certain unwanted biases in the information for the research. It can be observed that the research is completely based on the views of other authors. There is over-dependence on what others say regarding the subject matter of the research. There is no new addition of data in such a method and therefore systematic review limits fresh perspectives in research.
The changing conditions in the educational environment and its digital aspects should be analysed by receiving fresh data. However, this is not possible in a systematic review. Also, it is difficult to analyse which material is necessary for systematic research since there is a lot of content available on the internet.
Despite the inclusion and exclusion criteria and a limit on the studies to be taken for the research, it is difficult to analyse which research is the best suitable for the content analysis. The screening process takes a lot of time in the systematic review and acts as a limitation for the effective analysis of data as per the decided time (Haddaway, et al., 2020).
The time limitations as well as the screening process time create a barrier for the author of the research and hence the quality of data collected might be impacted. Currently, the research observes the RSE program from the overall perspective of education in the UK.
There is no specific analysis of particular schools or universities. This limits the research from understanding how the school curriculum and teaching practices can have an impact on the RSE programs. Hence, there is a limitation on the choice of content that can be either selected or can be freshly generated using different ways of research data collection.
Certain recommendations are necessary as per the research findings. It is important for the education systems of RSE to have proper training and development of the teachers (Cumper, et al., 2023). The research by Cumper, et al. (2023) has highlighted many perspectives that show the lack of proper training for the teachers. Due to this, the teachers are not able to teach the information as it should be.
There is a difference between the teaching patterns of teachers in different schools. The lack of uniform measures created issues. Hence, it is important to properly train the teachers so that they can teach the RSE programs as per their sensitivity and also answer the doubts of the students (Cumper, et al., 2023). A proper budget should be allotted to the RSE programs so that there can be adequate resources for teaching these programs.
The lack of proper budget and its distribution is a challenge here and it leads to the lack of proper education regarding RSE programs (Holt, 2023). There is a need to ensure that the financial resources support the teachers as well as the learning material requirements of the RSE programs.
Also, it is essential to check how digital media is impacting the implementation of the RSE programs. Along with the learnings through digital media, digital media is also acting as an improper source of relationship and sexual education (Setty, 2023). Proper use of digital media should be covered in the syllabus of the RSE programs to make sure that the students get the right education from the right sources.
Future research regarding this topic can be done through the use of mixed methods. Also, allowing for a quantitative perspective and data collection can be more beneficial. Quantitative analysis would help the author of the research to gain new perspectives regarding the effectiveness of relationship and sexual health education for adolescents.
Since, there has been an increase in the use of digital media trends, having new data collection would help in gaining current perspectives regarding the effectiveness of the RSE programs and others.
Either future research can work on the importance of digital media in the RSE programs and how to control its misuse, or it can be based on an analysis of different educational institutes in the UK regarding their teaching status of RSE programs. These can be added as new objectives in future research.
It is essential to get authentic data on schools and the importance of RSE. Moreover, as per the terms of the RSE program, the calculation of the results of the first three years of RSE will be done in December ending or January 2024 (Government UK, 2023a).
The data provided by the official authorities of RSE in the near future can be used in future research. In addition, the analysis of the data provided by the RSE board can be useful in linking it with the results of this research and forming new recommendations.
Future research can also be completely based on the data calculated by the government of the UK regarding the success of RSE programs in its three years. The benefits and challenges can be explored on the basis of that data.
This research has included information from multiple authors and there is a detailed review of many research articles regarding relationship and sexual health education programs. This research has included detailed information about the RSE programs in the UK for adolescents. Therefore, it has positive implications for public health practices related to adolescents.
Sexual health issues and relationship health matters have been observed much more in the current time. Being related to the behaviours of students, it can also be helpful for the school authorities to make wise decisions related to relationships and sexual education and ensure that the digital media implications are considered as well.
A theme found in the research findings says that the RSE programs have information regarding diversity which includes gender and sexual minorities. Therefore, this research has found the importance of RSE programs in gender and minority-based education which can be also useful for public health authorities.
In understanding the behaviours of sexual minorities. This research offers valuable information for public health officials who want to understand the ongoing status of health-based information for students. Relationship and sexual health information related to adolescents is essential for the public health authorities since sexually transmitted diseases have to be controlled in the UK.
There is also a need to reduce teen pregnancy issues and it is an important concern for public health officials. Therefore, these officials can understand the core perspectives related to RSE in this research and also analyse if the program is effective for the students or not.
This research also highlights the importance of peer group discussions post the RSE lectures and that they have an impact on the thoughts of students. Relationship and sexual health matters are also related to the mental health of students.
Mental health is a rising issue in public health. The relationship and sexual health aspect can be understood by public health officials through this research and apply this information in the link to mental health. Another research theme highlights that digital media has an impact on the RSE programs since it affects the relationships and sexual information of the students.
Hence, the perspectives of digital media shared in this research can be used by public health authorities to develop their strategies to deal with the negative impact of digital impact.
Different sexually transmitted diseases and their impact on adolescents can also be analysed by using the information taught in the RSE programs. These aspects can be considered by the education board authorities as well.
Therefore, such research can help public health specialists explore the role of educational programs in guiding adolescent children in an effective way.
This research aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of school-based education programs on the relationship and sexual health of adolescents in the UK. To complete this aim, the research was divided into three objectives.
These include identifying the key elements of RSE programs and determining who is teaching them; assessing the implication of school-based health education courses on relationship dynamics and sexual risk behaviours of adolescents; and to analyse the actual implementation of the educational courses identified in the schools and their success rates and identifying any gaps in the provisions.
A detailed literature review was carried out on the same. To analyse the benefits and challenges of the RSE programs, the research used a systematic research format. A total of 12 studies by different authors were analysed in the data table. Through the analysis and discussion, it has been found that the research has been able to complete its objectives thoroughly.
Discussing the first objective, it has been evaluated in the research that the RSE program has been divided into primary and secondary information. Primary information is provided to primary classes which has a range of elements such as relationships with people in general, self-awareness, health, and others.
The secondary information is given to the senior students where topics such as sexual health, hormones, relationship matters, contraception, teenage pregnancy, sexually transmitted diseases, and other matters are discussed. Teachers are chosen as per their specifications regarding the subjects and it has been made necessary by the government of the UK to teach these programs in schools.
Now discussing the second objective, the research has found that there are positive impacts of the RSE program on students. RSE leads to informed decision-making in the students and they are able to better understand the matters associated with relationship and sexual health.
This has also helped in reducing teenage pregnancy matters and reducing sexually transmitted diseases. The authors of the research articles analysed here have also stated that a lack of educational support for relationship and sexual matters may lead to wrong decisions. This can either increase the chance of accessing adult content for the information or get negatively influenced by peer groups.
Having educational support for relationships and sexual matters ensures that the students are able to achieve a state of thought process where they can make informed and safe decisions regarding sexual affairs. In addition, since the RSE programs cover a range of topics including relationship building, self-awareness, being aware of self biologically, and also having knowledge about the protective measures against unsafe sexual activities, the students are able to make informed decisions.
Now discussing the implementation of these programs in schools and universities related to adolescent teachings, this research evaluated certain gaps in the effect of the RSE program.
There is a gap found between the presence of RSE programs and their actual impact on the students. Multiple gaps have been found in the research. It has been analysed that the teachers of these programs require support for delivering their educational topics.
It is essential to have a system of training for the teachers so that they can effectively teach the sensitive topics related to the RSE programs. Training of the teachers regarding the programs has been identified as a major challenge in the RSE programs in schools.
Additionally, the research has analysed that many schools are not considering the necessity of teaching this program. Different students have different perspectives regarding the impact of the RSE programs.
As per the research studies analysed, some students agree that the schools have taught them while some other students agree that they do not know much about the RSE programs. This highlights a difference between the implementation of the RSE programs in different educational settings.
In relation to this aspect, the research has also highlighted that there are budgetary issues regarding the implementation of the RSE programs. Budgetary issues are also reflected in the lack of training and development sessions, educational resources, and others.
Along with the above-mentioned challenges, the presence of digital media has also emerged as a considerable challenge. The practices related to digital media and its impact on RSE have to be made more precise.
The involvement of parents in the learning of the RSE programs is also an important element discussed in the research. RSE programs can have a better impact on the students if their parents take the initiative to make those topics understandable to their children and communicate about relationships and sexual health matters.
This research states that the students are not utilizing the information provided in the RSE program. Rather they are being aware of these sensitive matters through digital data.
A high share of information is being taken from the wrong sources of porn. This is a risky situation for the understanding of the RSE programs. Therefore, it is essential to find some digital solutions for the RSE program makers.
A positive aspect of the RSE programs has also been discussed in different research articles used in this dissertation. It was highlighted by one of the researchers that the RSE programs are good at maintaining updates.
There have been certain updates in the curriculum regarding the matters associated with LGBTQ+. The inclusion of such topics improves the acceptance of diversity.
As stated in the research, understanding sexual education from diverse perspectives helps to achieve a better understanding of relationships. Another aspect that was highlighted in the research is that the RSE programs were updated as per the needs of the external environment factors.
During COVID-19 lockdowns, the teachers were able to effectively update the program and teach using digital resources that ensured continuity for the RSE programs. This shows that the programs are designed in a way that they can be taught through both digital and classroom teaching methods. Moreover, there is a good scope for updating the topics as and when needed.
It has been also shared in the research that a lack of information regarding relationships and sexual health can increase sexual health issues and transmitted diseases.
While, with educational support, a student can deal with such situations in a much better way and prevent themselves from such diseases. The research has stated that sexual risk behaviours can be developed in adolescents if they are not educated about the topics.
They can be easily influenced by their friend circle, background, country, and other beliefs. Therefore, having RSE information can shape their influence in a positive way and help them in making critical decisions.
Therefore, the objectives of this research were discussed separately in the literature review. To add more details to the research, the use of the data extraction method on the available research with respect to the UK provided further details regarding RSE programs.
Overall, this research has discussed multiple aspects related to the relationship and sexual health education for adolescents in the UK and the effectiveness of these programs.
Completing this dissertation has been one of its experiences. I have realized the importance of multiple research aspects that have to be considered when doing research. Different skills and knowledge have been developed through this research.
For example, my teacher evaluated the research on a timely basis which helped me in understanding the areas where I was not able to write the correct information. It made me understand the critical skills of creating a research up-to-date with recent information.
Using the latest data has made me stick to evaluating information as correctly as possible. I was able to develop critical decision-making skills through this research. As per the guidance given by my teacher, I analysed each aspect of the research again and again. This brought me clearance on many aspects of research such as the literature review and the research methods.
The skill and importance of using to-the-point data were developed through this research. Moreover, using a systematic approach helped me in analysing the research articles done by different authors in detail. Through this, I was able to get a look at the current situation regarding the RSE programs and the elements that make it a serious affair to be adopted in schools.
I have also developed a knowledge of research ethics when conducting this dissertation. Research ethics plays a crucial role in the successful creation of authentic research. For example, I ensured that the data collection method of this research will use only sources that are publicly available to all. No personal source was used by the author to maintain the sensitivity of the data associated with the adolescents (MacDonald, et al., 2023).
The available data sources have been screened through ethical requirements. Also, the research ensured that the data analysed was only used for the purpose of the research and no other reasons. Every data is being used as per their suitability with the research objectives.
The research did not aim to blame any school or educational course. It presented analysis of the effectiveness of such programs on the basis of the information publicly available on authentic databases and government websites.
Since the RSE programs are bounded by the government, I was able to understand that writing any wrong information in the research can make me liable for spreading wrong information. Therefore, I understood the importance of authenticity when conducting this dissertation.
Through this dissertation, I have been able to understand one of the most relevant topics of the current public health care that is relationship and sexual health. With the rise in sources of information, there has been an increase in the chances of accessing information regarding sexual matters through the wrong means. Doing this research has made me aware of many facts related to the benefits and challenges of the RSE programs.
When working as a public health professional in the future, I will ensure that I check the educational background of the people so that I am able to understand the causes behind their health matters. This research has helped me understand the difference between creating a program and its actual implementation ground level.
I have felt that it is necessary to keep tracking the success of an initiative so that proper corrective measures can be taken. Therefore, when practicing public health, I would try my best to work on the underlying causes of public health matters rather than just providing an overall perspective.
Alharahsheh, H.H. and Pius, A. (2020). A review of key paradigms: Positivism VS interpretivism. Global Academic Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, 2(3), pp.39-43.https://gajrc.com/media/articles/GAJHSS_23_39-43_VMGJbOK.pdf
Aventin, Á., Gough, A., McShane, T., Gillespie, K., O’Hare, L., Young, H., Lewis, R., Warren, E., Buckley, K. and Lohan, M. (2020). Engaging parents in digital sexual and reproductive health education: evidence from the JACK trial. Reproductive health, 17(1), pp.1-18. https://reproductive-health-journal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12978-020-00975-y
BASHH. (2023). New STI data for England reinforces the urgency of government commitment to prioritizing sexual health services. [Online] Available at: https://www.bashh.org/news/news/new-sti-data-for-england-reinforces-urgency-of-government-commitment-to-prioritising-sexual-health-services/ [Accessed 24th November, 2023].
Bauer, G.R., Churchill, S.M., Mahendran, M., Walwyn, C., Lizotte, D. and Villa-Rueda, A.A. (2021). Intersectionality in quantitative research: A systematic review of its emergence and applications of theory and methods. SSM-population health, 14, p.100798.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352827321000732
Bishop, M.D., Mallory, A.B., Gessner, M., Frost, D.M. and Russell, S.T. (2021). School-based sexuality education experiences across three generations of sexual minority people. The Journal of Sex Research, 58(5), pp.648-658. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00224499.2020.1767024
Bragg, S., Ponsford, R., Meiksin, R., Lohan, M., Melendez‐Torres, G.J., Hadley, A., Young, H., Anne Barter, C., Taylor, B. and Bonell, C. (2022). Enacting whole‐school relationships and sexuality education in England: Context matters. British Educational Research Journal, 48(4), pp.665-683. https://doi.org/10.1002/berj.3788
Braun, V. and Clarke, V. (2022). Conceptual and design thinking for thematic analysis. Qualitative Psychology, 9(1), p.3.https://psycnet.apa.org/journals/qua/9/1/3/
Cave, S. and Nicole. N. (2023). A Qualitative Exploration of Children and Young People’s Experiences of the Secondary Relationships and Sex Education Curriculum (Doctoral dissertation, University of Nottingham).
Chen, J.M. and Luetz, J.M. (2020) Mono-/inter-/multi-/trans-/anti-disciplinarity in research. Quality Education, pp.562-577.https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/978-3-319-95870-5_33.pdf
Children’s Commission. (2023). Children and RSHE. [Online] Available at: https://www.childrenscommissioner.gov.uk/blog/children-and-rshe/ [Accessed on 27th November 2023].
Cumper, P., Adams, S., Onyejekwe, K. and O’Reilly, M. (2023). Teachers’ perspectives on relationships and sex education lessons in England. Sex Education, pp.1-17.
Doyle, L., McCabe, C., Keogh, B., Brady, A. and McCann, M. (2020). An overview of the qualitative descriptive design within nursing research. Journal of Research in Nursing, 25(5), pp.443-455.https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/1744987119880234
Ferfolja, T. and Ullman, J. (2020). Gender and sexuality diversity in a culture of limitation: Student and teacher experiences in schools (p. 174). Taylor & Francis.https://library.oapen.org/handle/20.500.12657/52775 Holt, S.P., 2023. Mapping the reality of relationshop and sex education in the UK: A phenomenographic exploration of stakeholder conceptions regarding religious and political issues affecting a school’s implementation of policy. https://gupea.ub.gu.se/handle/2077/77248
Government UK. (2021). Relationships and sex education (RSE) and healthy education. [Online] Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/relationships-education-relationships-and-sex-education-rse-and-health-education [Accessed 7th December, 2023].
Government UK. (2023a). Delivery and teaching strategies [Online] Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/relationships-education-relationships-and-sex-education-rse-and-health-education/delivery-and-teaching-strategies [Accessed 7th December, 2023].
Government UK. (2023b). Relationships education (Primary) [Online] Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/relationships-education-relationships-and-sex-education-rse-and-health-education/relationships-education-primary [Accessed 7th December, 2023].
Government UK. (2023c). Relationships and Sex education (RSE) (Secondary) [Online] Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/relationships-education-relationships-and-sex-education-rse-and-health-education/relationships-and-sex-education-rse-secondary [Accessed 7th December, 2023].
Haddaway, N.R., Bethel, A., Dicks, L.V., Koricheva, J., Macura, B., Petrokofsky, G., Pullin, A.S., Savilaakso, S. and Stewart, G.B. (2020). Eight problems with literature reviews and how to fix them. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 4(12), pp.1582-1589.https://www.nature.com/articles/s41559-020-01295-x
Holt, S.P., (2023). Mapping the reality of relationshop and sex education in the UK: A phenomenographic exploration of stakeholder conceptions regarding religious and political issues affecting a school’s implementation of policy. https://gupea.ub.gu.se/handle/2077/77248
Horan, C., Stephenson, J. and Bailey, J.V. (2023). Relationships and Sex Education teaching in English secondary schools and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. Sex Education, pp.1-13.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/14681811.2023.2267449
Janssens, A., Blake, S., Allwood, M., Ewing, J. and Barlow, A. (2020). Exploring the content and delivery of relationship skills education programmes for adolescents: A systematic review. Sex Education, 20(5), pp.494-516.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/14681811.2019.1697661
Kaltiala, R., Bergman, H., Carmichael, P., de Graaf, N.M., Egebjerg Rischel, K., Frisén, L., Schorkopf, M., Suomalainen, L. and Waehre, A. (2020). Time trends in referrals to child and adolescent gender identity services: a study in four Nordic countries and in the UK. Nordic Journal of Psychiatry, 74(1), pp.40-44. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/08039488.2019.1667429
Levine, S.B., Abbruzzese, E. and Mason, J.W. (2022). Reconsidering informed consent for trans-identified children, adolescents, and young adults. Journal of Sex & Marital Therapy, 48(7), pp.706-727. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/0092623X.2022.2046221
Long, H.A., French, D.P. and Brooks, J.M. (2020). Optimising the value of the critical appraisal skills programme (CASP) tool for quality appraisal in qualitative evidence synthesis. Research Methods in Medicine & Health Sciences, 1(1), pp.31-42. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/2632084320947559
Long, R. (2023). Relationships and Sex Education in Schools (England). [Online] Available at: https://commonslibrary.parliament.uk/research-briefings/sn06103/ [Accessed on 24th November, 2023].
MacDonald, K.R., Enane, L.A., McHenry, M.S., Davis, N.L., Whipple, E.C. and Ott, M.A., (2023). Ethical Aspects of Involving Adolescents in HIV research: A Systematic Review of the Empiric Literature. The Journal of Pediatrics, p.113589.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022347623004523
Mardiana, S. (2020). Modifying Research Onion for Information Systems Research. Solid State Technology, 63(4), pp.5304-5313.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Siti-Mardiana/publication/359542575_Modifying_Research_Onion_for_Information_Systems_Research/links/62432dc07931cc7ccf033406/Modifying-Research-Onion-for-Information-Systems-Research.pdf
Maslowski, K., Biswakarma, R., Reiss, M.J. and Harper, J., (2022). Sex and fertility education in England: an analysis of biology curricula and students’ experiences. Journal of Biological Education, pp.1-19. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/00219266.2022.2108103
Mattimoe, R., Hayden, M., Murphy, B. and Ballantine, J. (2021). Approaches to analysis of qualitative research data: A reflection on the manual and technological approaches. Accounting, Finance & Governance Review, 27(1), pp.1-16.https://mural.maynoothuniversity.ie/17843/
McKellar, K. and Sillence, E. (2020). Teenagers, sexual health information and the digital age. Academic Press. https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=pGbIDwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=age+group+peer+group+pressure+on+sexual+health+adolescents&ots=WzJNNikZCm&sig=XSFsoPCBt0W-iooiy7COWuB_TzA
Meiksin, R., Campbell, R., Crichton, J., Morgan, G.S., Williams, P., Willmott, M., Tilouche, N., Ponsford, R., Barter, C.A., Sweeting, H. and Taylor, B. (2020). Implementing a whole-school relationships and sex education intervention to prevent dating and relationship violence: evidence from a pilot trial in English secondary schools. Sex education, 20(6), pp.658-674. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/14681811.2020.1729718
Mezmir, E.A. (2020). Qualitative data analysis: An overview of data reduction, data display, and interpretation. Research on humanities and social sciences, 10(21), pp.15-27.https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/356684456.pdf
Mohamed Shaffril, H.A., Samsuddin, S.F. and Abu Samah, A. (2021). The ABC of systematic literature review: the basic methodological guidance for beginners. Quality & Quantity, 55, pp.1319-1346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-020-01059-6
National Institutes of Health. (2023). Sexual Assault in Adolescents. [Online] Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7702185/ [Accessed on 24th November, 2023].
National Institutes of Health. (2023). Sexuality, Sexual Health, and Sexually Transmitted infections in adolescents and young adults. [Online] Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7482983/ [Accessed on 24th November, 2023].
Opara, I., Rodas, E.I.R., Garcia-Reid, P. and Reid, R.J. (2020). Ethnic identity, empowerment, social support and sexual risk behaviors among black adolescent girls: examining drug use as a mediator. Child and Adolescent Social Work Journal, pp.1-16. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/15248399231171145
Paul, J. and Barari, M. (2022). Meta‐analysis and traditional systematic literature reviews—What, why, when, where, and how?. Psychology & Marketing, 39(6), pp.1099-1115. https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.21657
Ponsford, R., Meiksin, R., Bragg, S., Crichton, J., Emmerson, L., Tancred, T., Tilouche, N., Morgan, G., Gee, P., Young, H. and Hadley, A., (2021). Co-production of two whole-school sexual health interventions for English secondary schools: positive choices and project respect. Pilot and feasibility studies, 7(1), pp.1-17. https://pilotfeasibilitystudies.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40814-020-00752-5
Pratt-Chapman, M.L. (2020). Implementation of sexual and gender minority health curricula in health care professional schools: a qualitative study. BMC Medical Education, 20, pp.1-14. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12909-020-02045-0
PSHE. (2023). What data and resources do teachers need to support statutory health education? [Online] Available at: https://pshe-association.org.uk/news/news-and-blog/blog-entry/what-data-and-resources-do-teachers-need-support [Accessed 27th November, 2023].
Purcell, C., McDaid, L., Forsyth, R., Simpson, S.A., Elliott, L., Bailey, J.V., Moore, L. and Mitchell, K.R., (2023). A peer-led, school-based social network intervention for young people in the UK, promoting sexual health via social media and conversations with friends: intervention development and optimisation of STASH. BMC Public Health, 23(1), p.675.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12889-023-15541-x
Queiroz, J.F., Medeiros, K.S., Sarmento, A.C.A., Monteiro, M.N., Cobucci, R.N., Stransky, B. and Gonçalves, A.K. (2020). Use of dating sites and applications by women and their risk of sexually transmitted infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis protocol. BMJ open, 10(11), p.e038738. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2020-038738
Setty, E. (2023). Digital media and relationships, sex, and health education in the classroom. Pastoral care in education, 41(3), pp.289-305. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/02643944.2022.2095418
Setty, E. and Dobson, E. (2023). Department for Education Statutory Guidance for Relationships and Sex Education in England: A Rights-Based Approach?. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 52(1), pp.79-93.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10508-022-02340-5
Sex Education Forum. (2023). New policy shows young people are being failed by poor relationships and sex education in schools and at home. [Online] Available at: https://www.sexeducationforum.org.uk/news/news/new-polling-shows-young-people-are-being-failed-poor-relationships-and-sex-education [Accessed on 24th November, 2023].
Slattery, P., Saeri, A.K. and Bragge, P. (2020). Research co-design in health: a rapid overview of reviews. Health research policy and systems, 18(1), pp.1-13.https://health-policy-systems.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12961-020-0528-9
Staff, K., Principal, A.P., Pastoral, H. and Directors, P. (2023). Relationships & Sex Education (Rse) Policy. https://worthgateschool.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/RSE-Policy.pdf
Statista. (2023). Share of sexually transmitted infections diagnosed among young people in England in 2020. [Online] Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/654038/sexually-transmitted-infections-sti-breakdown-amoung-youth-england/#:~:text=Sexually%20transmitted%20infections%20diagnosed%20among%20young%20people%20in%20England%202020&text=This%20statistic%20displays%20the%20share,the%20chlamydia%20diagnoses%20in%20England [Accessed 27th November, 2023].
Strijker, D., Bosworth, G. and Bouter, G. (2020). Research methods in rural studies: Qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods. Journal of Rural Studies, 78, pp.262-270.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S074301671830740X
Tahir, I. (2022). The UK education system preserves inequality – new report. [Online] Available at: https://ifs.org.uk/articles/uk-education-system-preserves-inequality-new-report [Accessed 27th November, 2023].
Ugwu, C.N. and Opah, A.C. (2023). Use of Boolean search strategy for accessing the databases of university of technology libraries by postgraduate students. Journal of Library Services and Technologies, 5(2), pp.24-35.https://credencepressltd.com/journal/uploads/archive/202316950429705722016419.pdf
Uttley, L., Quintana, D.S., Montgomery, P., Carroll, C., Page, M.J., Falzon, L., Sutton, A. and Moher, D. (2023). The problems with systematic reviews: a living systematic review. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0895435623000112
van Leent, L., Walsh, K., Moran, C., Hand, K. and French, S. (2023). Effectiveness of relationships and sex education: A systematic review of terminology, content, pedagogy, and outcomes. Educational Research Review, p.100527.
Vears, D.F. and Gillam, L. (2022). Inductive content analysis: A guide for beginning qualitative researchers. Focus on Health Professional Education: A Multi-disciplinary Journal, 23(1), pp.111-127.https://search.informit.org/doi/abs/10.3316/informit.455663644555599
Wilder, R., (2023). Power, authority and expertise: policy making about relationships and sex education in English primary schools. Journal of Education Policy, 38(5), pp.782-802. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/02680939.2022.2028309
Wood, S.K., Ford, K., Madden, H.C., Sharp, C.A., Hughes, K.E. and Bellis, M.A. (2022). Adverse childhood experiences and their relationship with poor sexual health outcomes: results from four cross-sectional surveys. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(14), p.8869. https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/19/14/8869
Are you confident that you will achieve the grade? Our best Expert will help you improve your grade
Order Now










